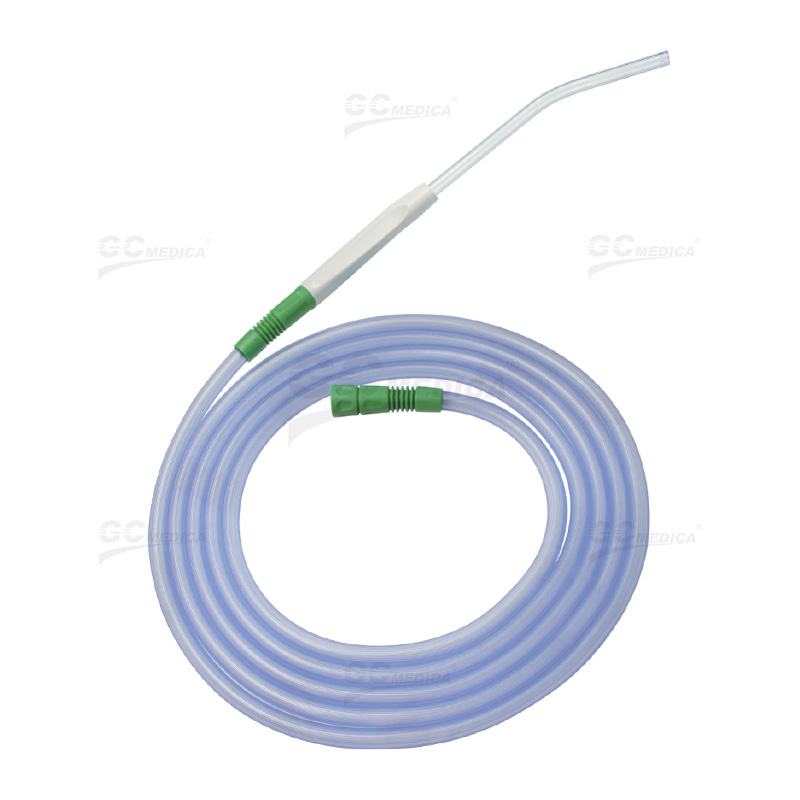
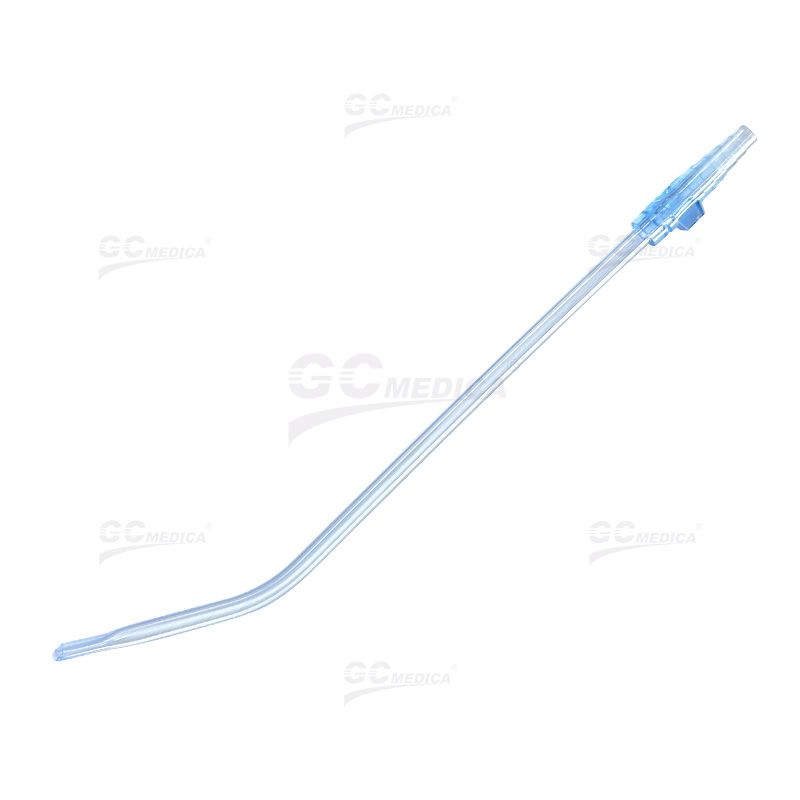
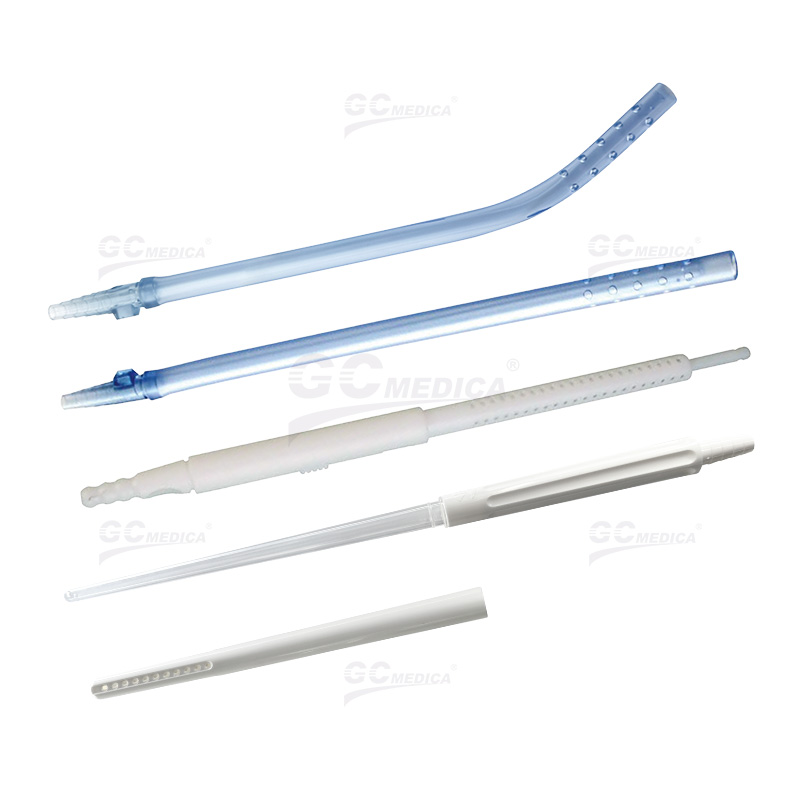
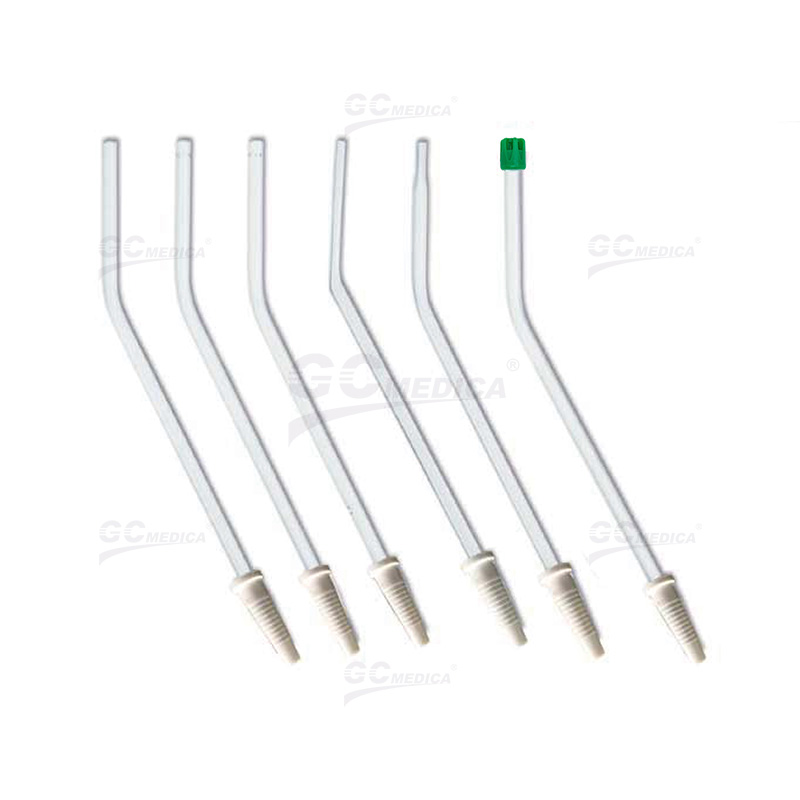
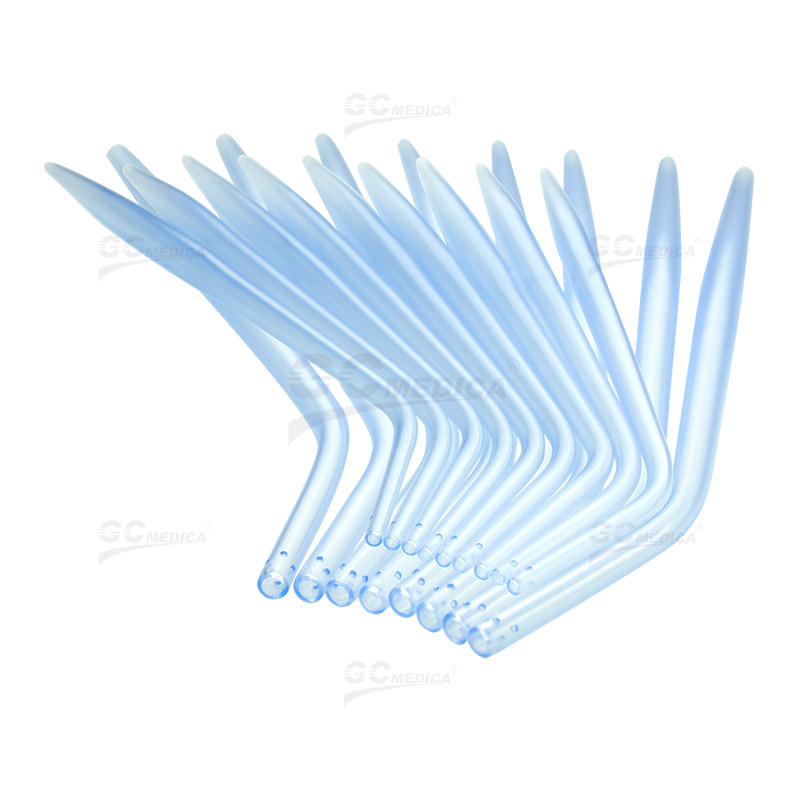
The Yankauer suction tip, developed in 1907 by Dr. Charles Yankauer, is a widely used medical instrument designed for effective suctioning of oropharyngeal secretions without causing tissue damage. It is commonly utilized to prevent aspiration and maintain a clear surgical field during procedures. Yankauer suction tips are primarily categorized into two types based on their design: vented and non-vented. Understanding the differences between these two variants is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
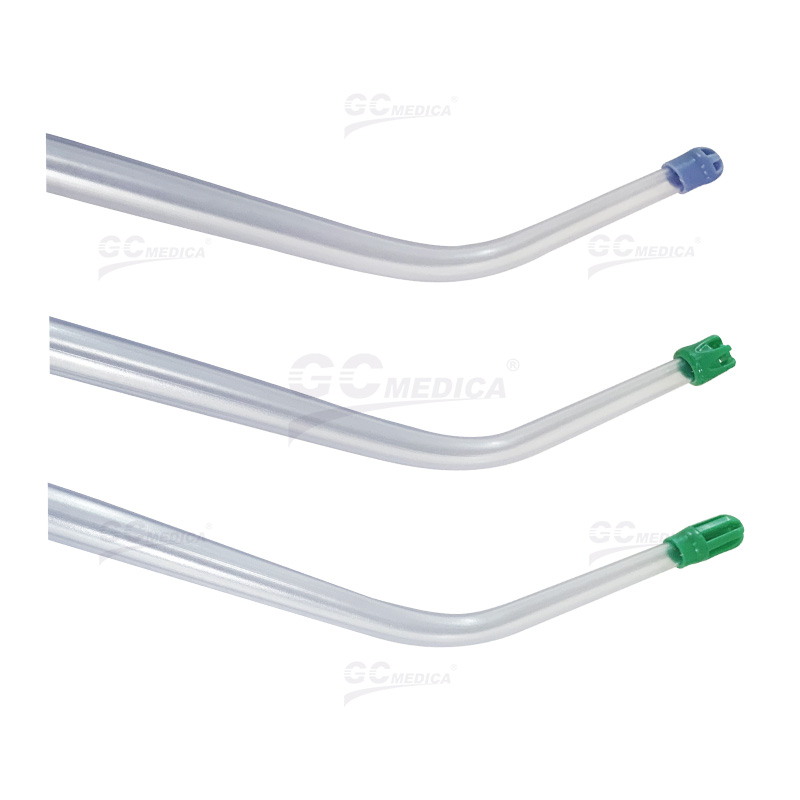
Vented Yankauer Suction Tips
Vented Yankauer suction tips are equipped with a small air vent, typically located on the handle. This vent allows clinicians to regulate the suction pressure manually by covering or uncovering the vent with a finger during the procedure. The key features and benefits include:
Suction Control: The vent provides the ability to modulate suction intensity, allowing for gentle aspiration when needed. This is particularly beneficial when working in delicate areas to minimize tissue trauma.
Patient Comfort: By adjusting the suction pressure, vented tips can enhance patient comfort during procedures, reducing the likelihood of mucosal damage.
Versatility: The adjustable suction makes vented tips suitable for a variety of procedures, from routine oral care to more sensitive surgical interventions.
However, it's important to note that the effectiveness of vented tips relies on the clinician's ability to appropriately manage the vent during use.
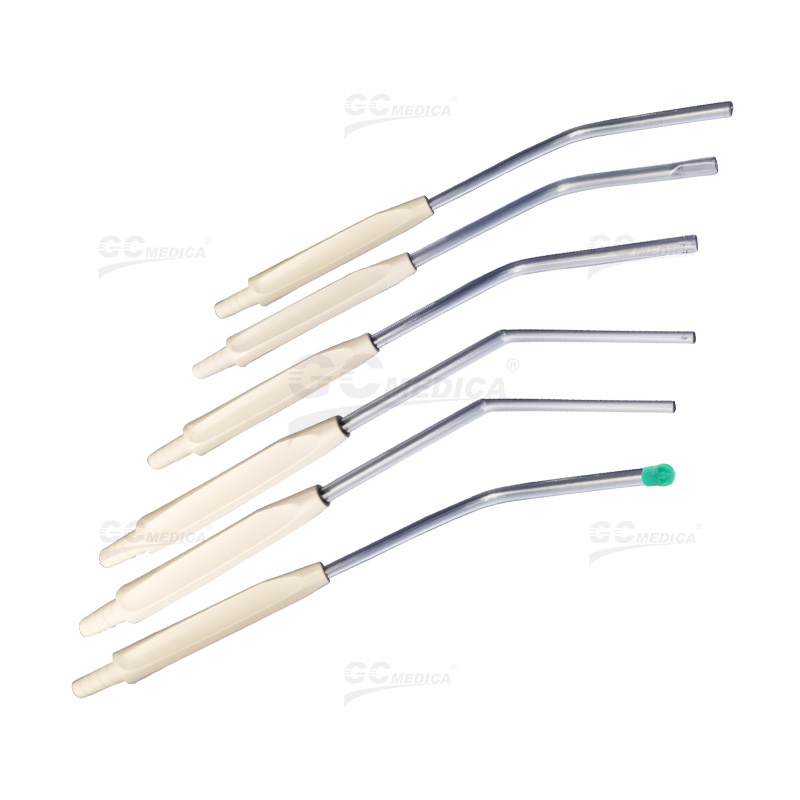
Non-Vented Yankauer Suction Tips
In contrast, non-vented Yankauer suction tips lack an air vent, resulting in continuous, unregulated suction when connected to a vacuum source. Characteristics of non-vented tips include:
Consistent Suction: They provide a steady suction force, which can be advantageous in situations requiring rapid removal of fluids or debris.
Simplicity: Without the need to manage a vent, these tips offer straightforward operation, which can be beneficial in emergency scenarios where time is critical.
Specific Applications: Non-vented tips are often preferred in procedures where continuous suction is necessary, and the risk of tissue damage is minimal.
However, the lack of suction control may increase the risk of tissue trauma, especially in sensitive areas.
Clinical Considerations
When choosing between vented and non-vented Yankauer suction tips, healthcare providers should consider the following factors:
Procedure Type: For procedures involving delicate tissues or requiring precise suction control, vented tips are preferable. Non-vented tips may be more suitable for rapid fluid evacuation in less sensitive areas.
Patient Condition: Patients with fragile mucosa or those prone to bleeding may benefit from the adjustable suction provided by vented tips.
Clinician Experience: Proper use of vented tips requires familiarity with suction modulation techniques. Clinicians should be trained to use the vent effectively to prevent inadvertent tissue injury.
Infection Control: Both vented and non-vented tips are available in disposable and reusable forms. Disposable tips are recommended to minimize cross-contamination risks.
Conclusion
The choice between vented and non-vented Yankauer suction tips should be guided by the specific clinical scenario, patient needs, and the healthcare provider's proficiency with the instrument. Vented tips offer adjustable suction control, enhancing safety and comfort during procedures involving delicate tissues. Non-vented tips provide consistent suction, suitable for rapid fluid removal in appropriate contexts. By selecting the appropriate suction tip, clinicians can optimize procedural outcomes and uphold the highest standards of patient care.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us