Gastric lavage, commonly referred to as "stomach pumping," is a critical medical procedure used to empty the stomach contents in emergency and diagnostic scenarios. Understanding when gastric lavage is recommended helps healthcare providers make timely decisions to improve patient outcomes. Below, we explore its primary clinical applications and guidelines.
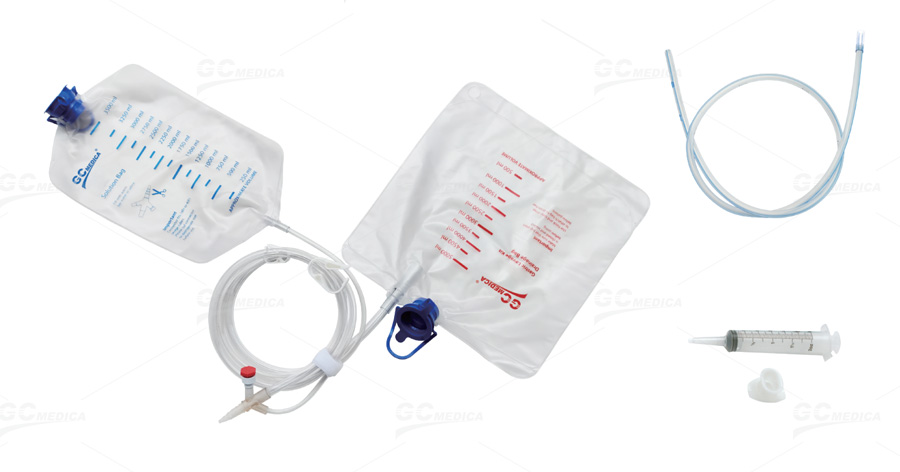
Gastric Wash Kit | GCMEDICA
What Is Gastric Lavage?
Gastric lavage involves inserting a tube through the mouth or nose into the stomach to administer fluids and remove toxic substances, undigested pills, or other harmful materials . This procedure is often performed in emergency departments and requires specialized equipment, such as sterile gastric tubes and lavage solutions .
Top 5 Clinical Indications for Gastric Lavage
1. Acute Poisoning or Drug Overdose
Gastric lavage is most frequently recommended for acute poisoning caused by ingesting toxic substances (e.g., pesticides, household chemicals) or drug overdoses (e.g., opioids, antidepressants). The procedure is most effective within 1-2 hours of ingestion to prevent toxin absorption into the bloodstream .
Example: A patient who accidentally consumes a lethal dose of medication may require immediate lavage to reduce systemic toxicity.
2. Preoperative Bowel Preparation
In gastrointestinal surgeries, lavage is used to cleanse the stomach or intestines before procedures. For instance, "whole gut lavage" with electrolyte solutions helps clear the digestive tract, minimizing surgical complications .
3. Diagnostic Sampling
Lavage aids in collecting gastric fluid samples for diagnosing infections (e.g., tuberculosis) or identifying bleeding sources. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is also used to analyze lung conditions .
4. Management of Corrosive Substance Ingestion
While controversial, lavage may be cautiously employed in cases of non-corrosive poison ingestion (e.g., alcohol, certain drugs). However, it is contraindicated for corrosive substances (e.g., acids, alkalis) to avoid esophageal or gastric perforation .
5. Pediatric and Animal Research Applications
In pediatric care, modified lavage techniques are used for children with accidental poisonings . Additionally, animal studies rely on lavage for toxicology research, emphasizing precise insertion depth and post-procedure monitoring.
Key Considerations and Contraindications
Timing Matters: Lavage is ineffective if performed >4 hours after ingestion due to gastric emptying .
Risks: Aspiration pneumonia, mucosal injury, and electrolyte imbalances may occur if not done correctly .
Alternatives: Activated charcoal administration is often preferred for certain toxins due to its safety profile .
Conclusion
Gastric lavage remains a vital intervention in emergencies involving toxic ingestions and preoperative preparation. Adherence to clinical guidelines—such as patient assessment, proper equipment sterilization, and post-procedure care—ensures safety and efficacy. For healthcare facilities, investing in high-quality lavage kits and staff training is essential to optimize outcomes.
By understanding these indications, medical professionals can better determine when gastric lavage is recommended and deliver life-saving care.
Keywords: gastric lavage, stomach pumping, gastric wash, gastric washing,stomach wash


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us