Feeding tubes play a crucial role in providing essential nutrition and hydration to patients who are unable to eat by mouth. This guide is designed to help patients and caregivers understand the basics of feeding tubes, how they work, and what to expect during treatment.
What Are Feeding Tubes?
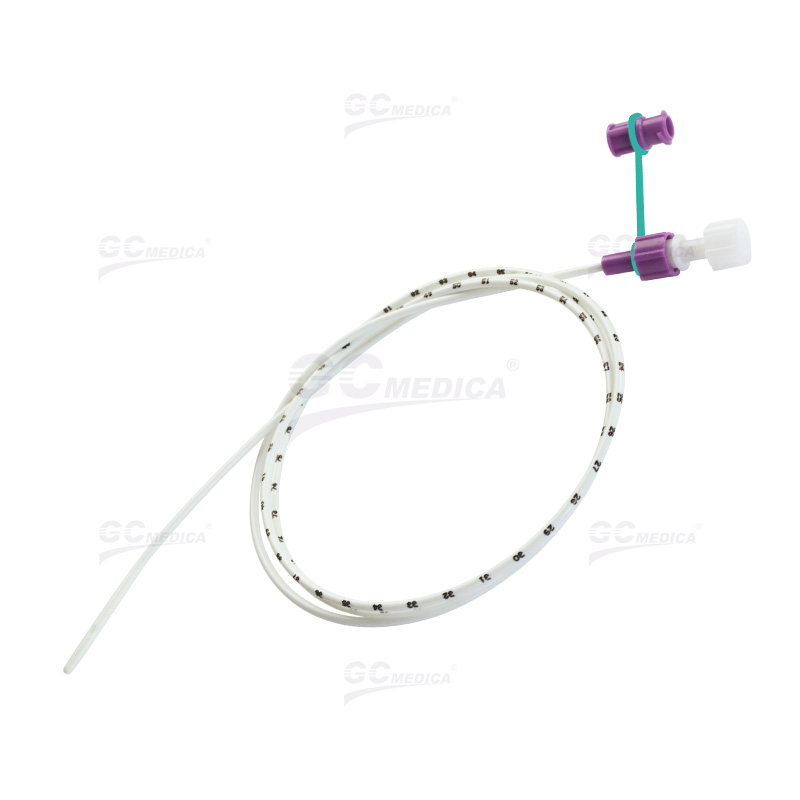
A feeding tube is a medical device inserted through the nose, mouth, or directly into the stomach or small intestine to deliver nutrition. They are used when a patient has difficulty swallowing, has a blocked digestive tract, or requires long-term nutritional support. Feeding tubes ensure that the body receives the necessary calories, vitamins, and minerals to promote healing and overall well-being.
| ENFit Polyurethane Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
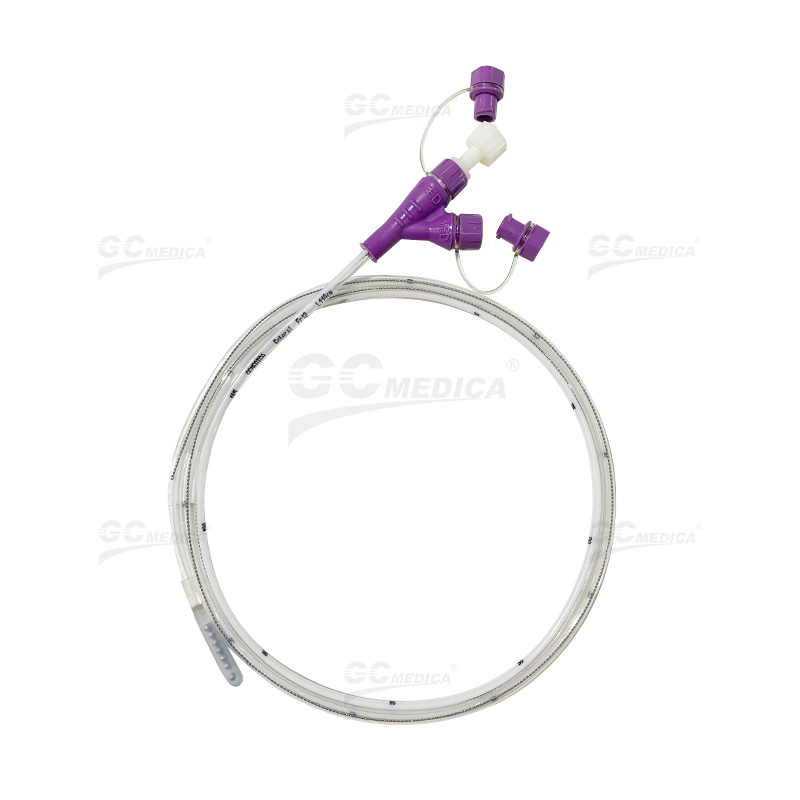
| ENFit Y-Port Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
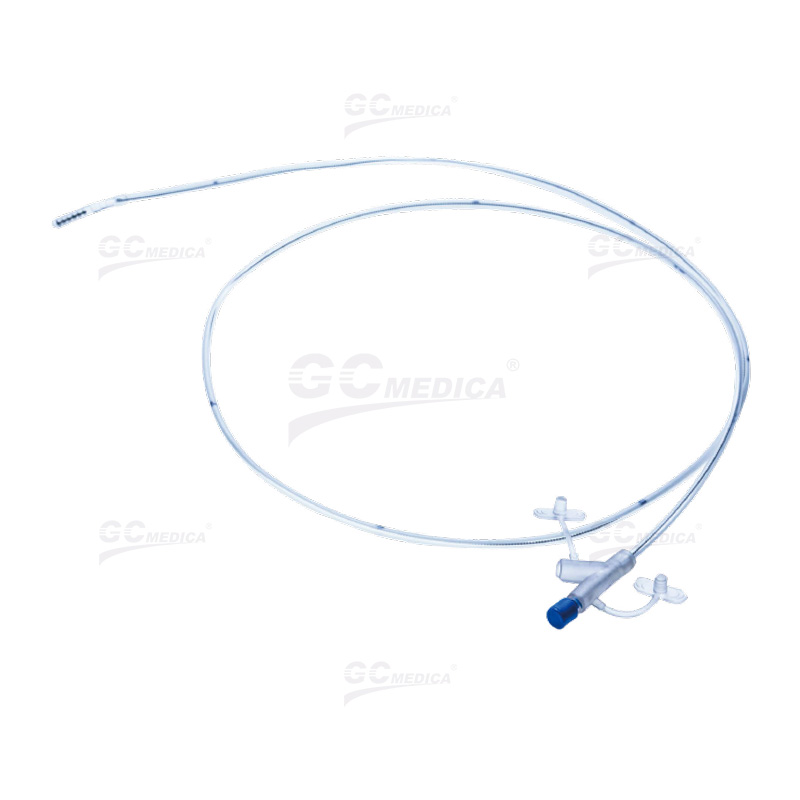
| Nasointestinal Feeding Tube | |
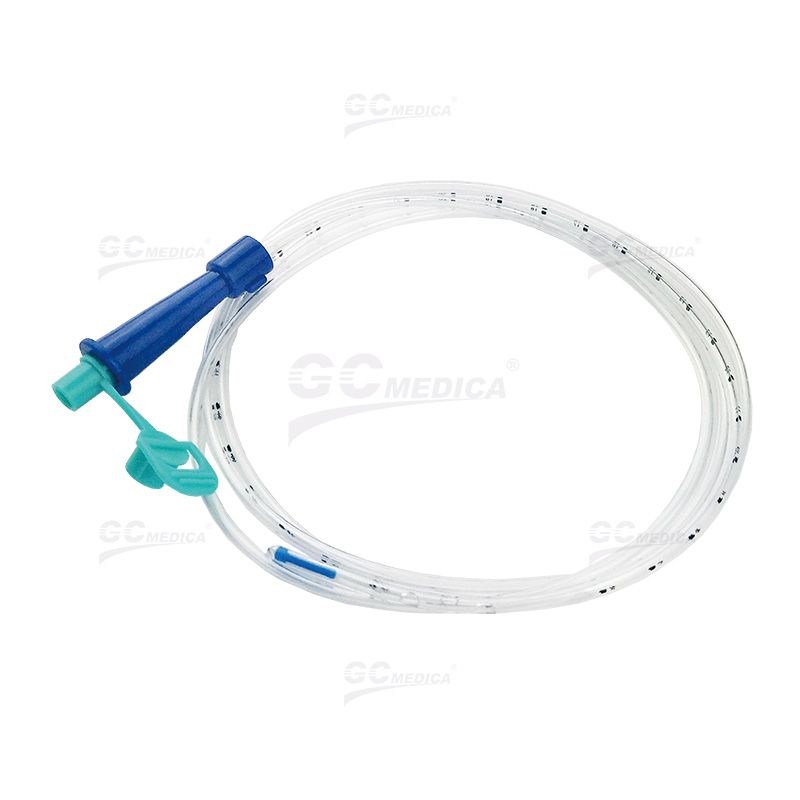
| Nasogastric (Ryles) Tubes |
Types of Feeding Tubes
There are several types of feeding tubes, each designed for specific needs:
Nasogastric (NG) Tube: Inserted through the nose into the stomach, this tube is typically used for short-term feeding.
Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube): Surgically placed directly into the stomach, G-tubes are ideal for long-term nutritional support.
Jejunostomy Tube (J-tube): This tube goes directly into the small intestine and is used when the stomach needs to be bypassed.
Understanding the differences between these tubes can help patients and caregivers decide which option best suits the individual’s medical needs.
When Is a Feeding Tube Needed?
Feeding tubes are recommended when patients face challenges such as:
Swallowing Difficulties: Conditions like stroke, neurological disorders, or head and neck cancers may impair swallowing.
Digestive Disorders: Diseases such as Crohn’s disease or gastrointestinal blockages can hinder nutrient absorption.
Post-Surgery Recovery: Patients recovering from surgery, particularly in the digestive tract, may temporarily require tube feeding.
A healthcare provider will assess the patient’s condition to determine whether a feeding tube is necessary and which type is most appropriate.
How Feeding Tubes Work
Feeding tubes deliver liquid nutrition directly into the stomach or small intestine. The nutritional formula is carefully measured to meet the patient’s specific dietary needs. There are two main methods for tube feeding:
Continuous Feeding: Nutrients are delivered slowly over several hours, which is ideal for patients who cannot tolerate large volumes at once.
Bolus Feeding: A set amount of nutrition is provided at intervals, mimicking regular meal times.
The choice between these methods depends on the patient’s medical condition and nutritional requirements.
Caring for a Feeding Tube
Proper care of a feeding tube is essential to prevent complications such as infections or blockages. Here are some best practices for tube maintenance:
Daily Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the tube and insertion site is vital to reduce infection risk.
Monitoring for Signs of Infection: Watch for redness, swelling, or discharge at the insertion site. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Regular Flushing: Flushing the tube with water as directed by a healthcare professional helps prevent clogs.
Safe Handling: Always handle the tube gently to avoid dislodging or damaging it.
For caregivers, understanding these steps can provide peace of mind and help maintain the patient’s health.
Potential Complications
While feeding tubes are generally safe, complications can occur. Common issues include:
Infection: At the insertion site or internally.
Clogging: Due to residue build-up in the tube.
Discomfort or Irritation: Sometimes experienced at the tube’s entry point.
Patients and caregivers should maintain open communication with healthcare providers to address any concerns early on.
Tips for Caregivers
Taking care of someone with a feeding tube can be challenging. Here are some practical tips:
Educate Yourself: Learn as much as you can about the specific type of feeding tube and its maintenance.
Establish a Routine: Consistent care routines can help ensure the tube is properly maintained.
Stay Organized: Keep a log of feedings, tube cleanings, and any issues that arise.
Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals or support groups for advice and emotional support.
Conclusion
Feeding tubes are an essential tool for providing nutrition and supporting recovery in patients who cannot consume food normally. With the right information and care, both patients and caregivers can manage feeding tubes effectively, ensuring a better quality of life. Always consult with healthcare providers for personalized advice and to address any concerns about tube feeding.
This comprehensive guide offers a clear understanding of feeding tubes, aiming to empower patients and caregivers with the knowledge needed for safe and effective use. By following the recommended practices and staying informed, you can help ensure the best possible outcomes for those relying on tube feeding.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us