Endoscopic procedures are essential for diagnosing and managing gastrointestinal conditions, particularly in detecting and treating polyps. A key component in these procedures is the use of a polyp trap, a device designed to capture polyps during endoscopy. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of polyp traps, best practices for their use, and the benefits they offer for optimal polyp collection and analysis.
 Polyp Trap for Endoscopy Online Promotion >
Polyp Trap for Endoscopy Online Promotion >
Understanding the Polyp Trap
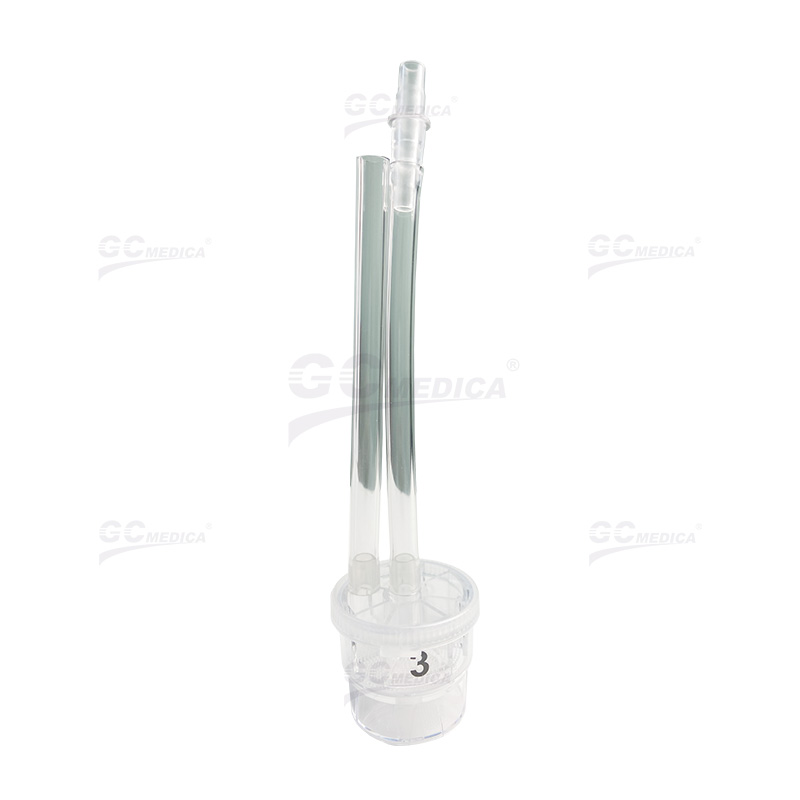
A polyp trap is a specialized accessory used during endoscopic examinations to capture polyps that are dislodged or removed from the gastrointestinal tract. Its primary function is to prevent polyps from being lost in the digestive system, ensuring that they can be accurately collected for pathological evaluation. By maintaining a secure capture of tissue samples, the polyp trap plays a critical role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Benefits of Using a Polyp Trap
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
Using a polyp trap improves the precision of endoscopic procedures by ensuring that all removed polyps are collected intact. This allows for thorough pathological analysis, which is crucial for early detection of precancerous conditions and gastrointestinal cancers. The ability to analyze polyps in detail contributes to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
Minimized Risk of Complications
Polyps that are not captured can travel further into the digestive system, leading to potential complications such as bowel obstruction or continued bleeding. The polyp trap minimizes this risk by securely capturing the tissue, thus preventing additional complications and ensuring patient safety.
Efficient Workflow in the Endoscopy Suite
Integrating a polyp trap into the endoscopic procedure streamlines the workflow. The trap allows for a smoother process by reducing the time spent on searching for lost tissue fragments. This efficiency not only improves patient outcomes but also optimizes the use of resources in busy clinical settings.
Best Practices for Optimal Polyp Collection and Analysis
Proper Device Setup and Handling
Before beginning the procedure, ensure that the polyp trap is correctly attached to the endoscope. Familiarize yourself with the device’s operation to guarantee smooth integration during the procedure. Proper handling and setup are crucial to prevent any dislodgement or loss of polyps during the examination.
Adherence to Aseptic Techniques
Maintaining strict aseptic techniques is essential during the use of a polyp trap. This includes using sterile equipment and following established protocols to reduce the risk of infection. Consistent adherence to these practices ensures that the collected tissue remains uncontaminated and suitable for accurate analysis.
Real-Time Monitoring During Procedures
Monitor the device in real-time to confirm that the polyp trap is functioning as intended. Continuous observation helps identify any issues early, such as improper positioning or blockage, allowing for immediate corrective actions. This proactive approach contributes to a more efficient and safe endoscopic procedure.
Comprehensive Training and Protocols
Healthcare providers should receive thorough training on the use of the polyp trap. Establish clear protocols that outline the steps for device setup, usage, and troubleshooting. Regular training and updates on best practices can help maintain high standards in tissue collection and overall endoscopy performance.
Conclusion
The integration of a polyp trap in endoscopic procedures represents a significant advancement in gastrointestinal diagnostics. By ensuring the optimal collection and analysis of polyps, these devices contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy, enhanced patient safety, and streamlined clinical workflows. Adopting best practices in device setup, aseptic techniques, real-time monitoring, and comprehensive staff training is essential for maximizing the benefits of the polyp trap. As healthcare continues to evolve, embracing these technologies and practices will play a crucial role in the early detection and management of gastrointestinal conditions


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us