Nasogastric tube (NGT) feeding is a critical intervention for adults who cannot meet nutritional needs orally due to medical conditions such as stroke, neurological disorders, or post-surgical recovery. This guide outlines evidence-based practices for safe and effective NGT feeding.
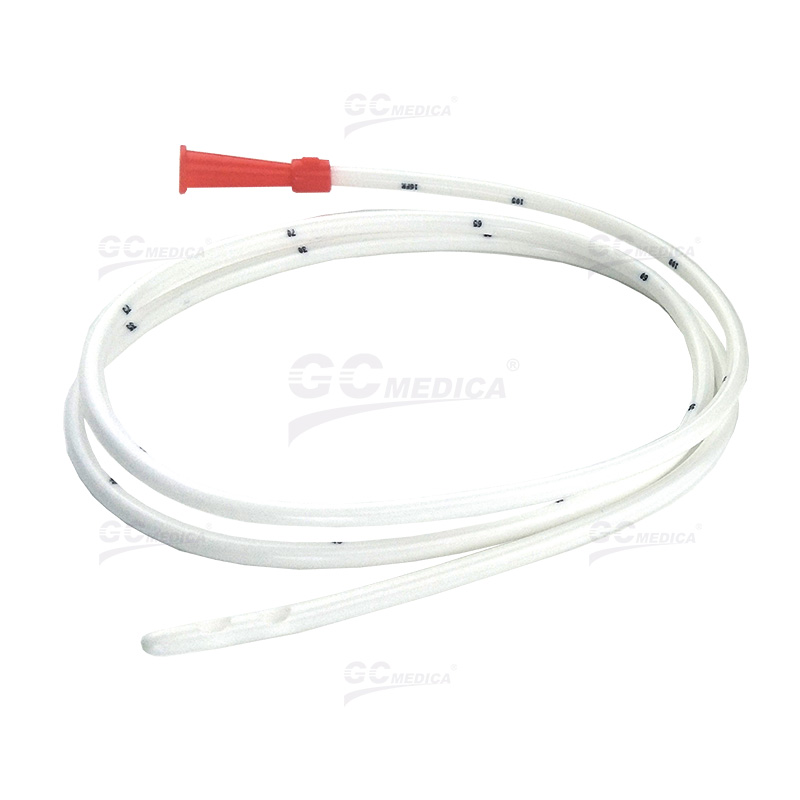
| Nasogastric tube | |
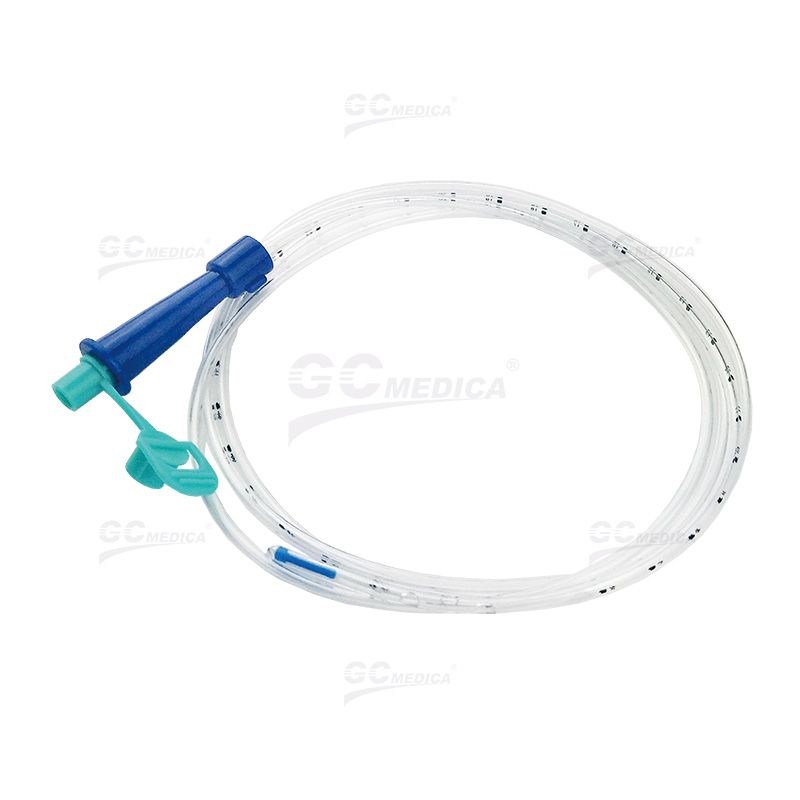
| Nasogastric feeding tube |
1. Indications and Patient Selection
NGT feeding is recommended for short-term nutritional support (typically 2-4 weeks) in adults with functional gastrointestinal systems but impaired swallowing or oral intake. Common candidates include stroke patients, those with head injuries, or individuals undergoing prolonged mechanical ventilation.
2. Tube Placement and Verification
Insertion: Use a sterile, flexible tube inserted through the nostril into the stomach. Ensure the patient’s head is elevated at 30-45 degrees during insertion.
Verification: Confirm placement via pH testing of aspirated gastric fluid (pH ≤5.5) or X-ray. Avoid auscultation alone due to inaccuracy.
3. Feeding Protocols
Formula Selection: Choose isotonic, nutritionally complete formulas based on caloric needs and medical conditions (e.g., diabetes-friendly or renal formulas).
Administration:
Bolus Feeding: Deliver 200-400 mL over 15-30 minutes, 4-6 times daily. Monitor for reflux.
Continuous Feeding: Use pumps for critically ill patients to reduce aspiration risk.
Flushing: Rinse the tube with 30-50 mL water before/after feeding and medication to prevent clogging.
4. Complication Prevention
Aspiration Risk: Maintain upright positioning during feeding and 1 hour post-feeding. Check residual volumes every 4-6 hours; withhold feeding if >250 mL.
Tube Displacement: Secure the tube with adhesive devices and avoid tension. Recheck placement if coughing/vomiting occurs.
Skin Care: Clean nostrils daily and rotate tube insertion sites to prevent pressure ulcers.
5. Special Considerations
Tracheostomized Patients: Exercise extreme caution during insertion to avoid respiratory misplacement.
Medication Administration: Crush non-enteric-coated pills finely and dissolve in water. Avoid mixing medications with formulas.
Conclusion
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe NGT feeding, minimizes complications, and optimizes patient outcomes. Regular training for caregivers and verification protocols are essential for success. For detailed clinical scenarios or product specifications, consult medical guidelines or trusted suppliers


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us