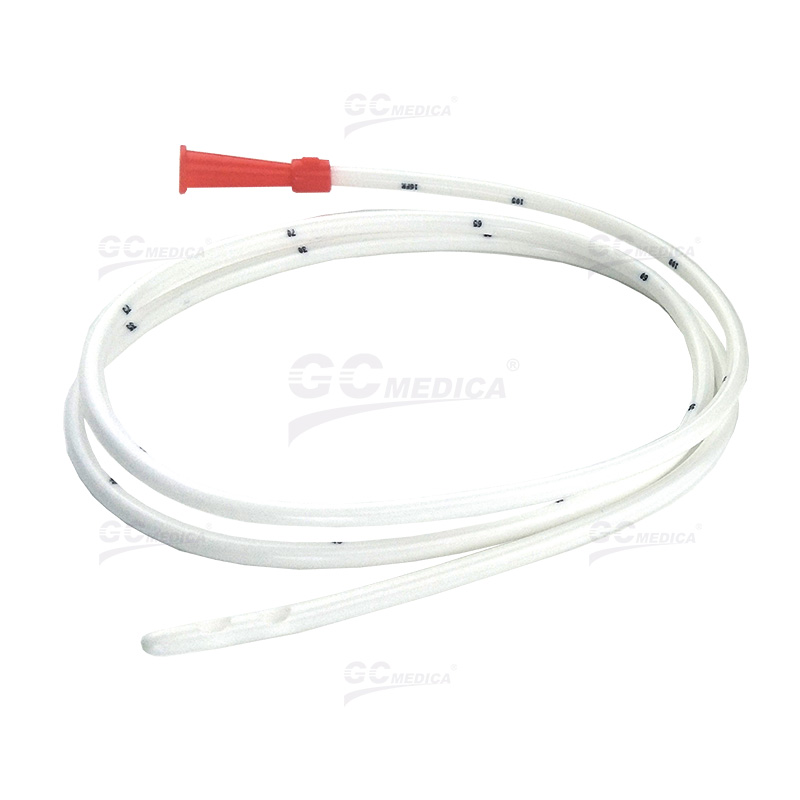
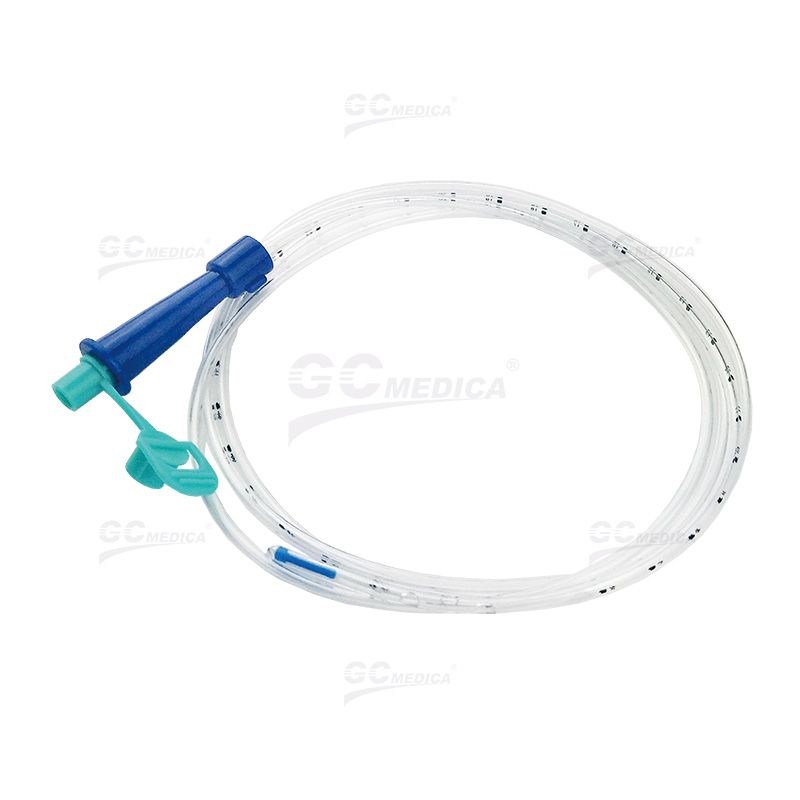
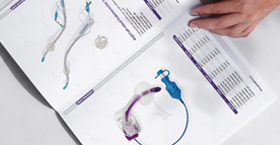
A nasogastric tube (NG tube) is a flexible medical device inserted through the nasal passage into the stomach, serving diagnostic and therapeutic purposes across diverse clinical scenarios. Its versatility makes it indispensable in modern healthcare, particularly for gastrointestinal management.
| Nasogastric tube | |
| Nasogastric feeding tube |
Key Functions and Uses
Nutritional Support: NG tubes deliver liquid nutrition, medications, or electrolytes directly to the stomach for patients unable to swallow, such as those recovering from stroke, surgery, or critical illness.
Decompression: Post-abdominal surgery, NG tubes alleviate gastric pressure by draining excess fluids or gas, reducing complications like vomiting or ileus.
Diagnostic Sampling: Gastric contents extracted via NG tubes aid in analyzing bleeding sources, pH levels, or infections.
Types and Placement
Common NG tube variants include Levin tubes (single-lumen) and Salem Sump tubes (double-lumen for simultaneous drainage and ventilation). Placement involves measuring the tube from the nose to the stomach, followed by verification via auscultation, pH testing, or imaging to prevent misplacement into the lungs.
Clinical Scenarios
Postoperative Care: NG tubes are routinely used after esophageal or gastrointestinal surgeries to prevent aspiration and promote healing.
Emergency Settings: In cases of poisoning or overdose, gastric lavage via NG tubes helps remove toxins.
Long-term Care: For patients with dysphagia or neurological disorders, NG tubes provide sustained nutritional support.
Risks and Precautions
Improper placement can lead to pneumothorax, aspiration, or mucosal damage. Prolonged use may cause sinusitis or throat irritation. Regular monitoring, tube flushing, and oral hygiene are critical to minimizing complications.
Conclusion
Nasogastric tubes remain a cornerstone in managing gastrointestinal dysfunction, offering life-sustaining benefits when used appropriately. Clinicians must balance efficacy with safety, adhering to evidence-based protocols for insertion and maintenance.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us