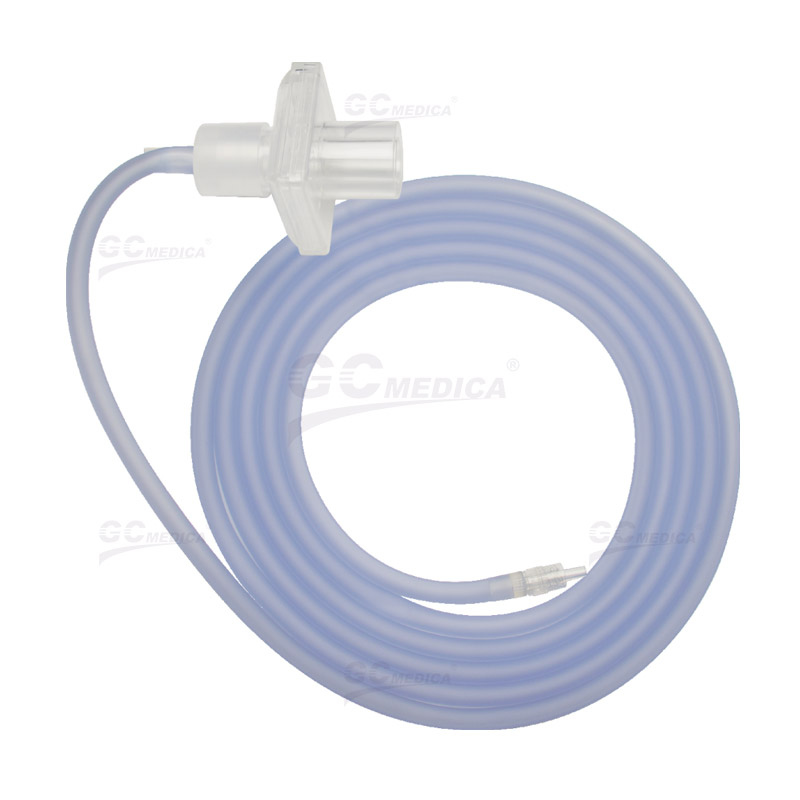
Insufflator tubing plays a crucial role in minimally invasive surgeries by delivering gas to create a pneumoperitoneum, providing surgeons with a clear view of the operative field. Proper selection and maintenance of insufflator tubing are essential to ensure patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes.
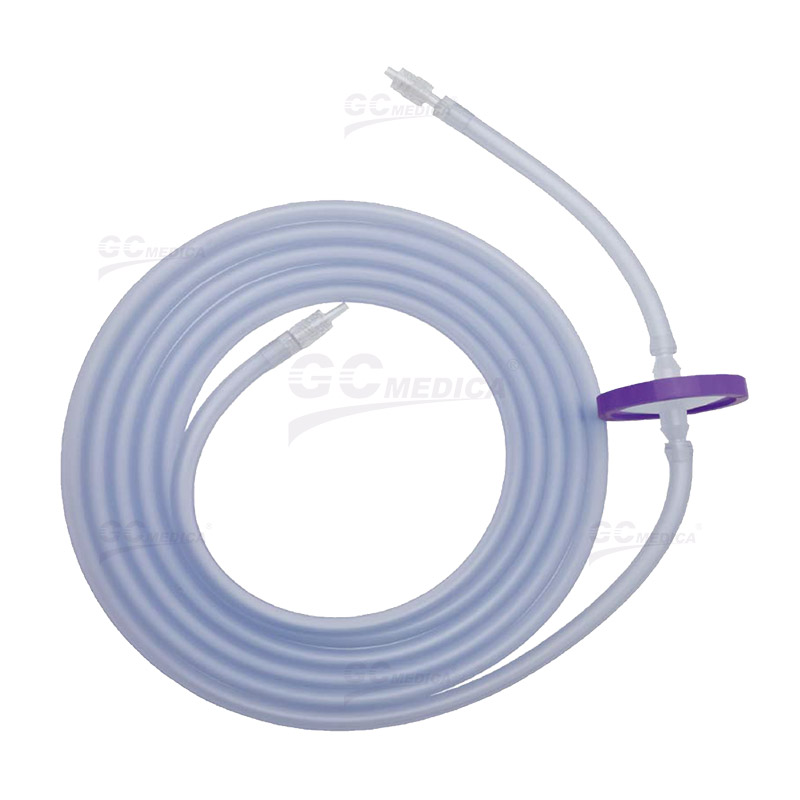
| Insufflator Tube | |
| Insufflation Tubing Set | |
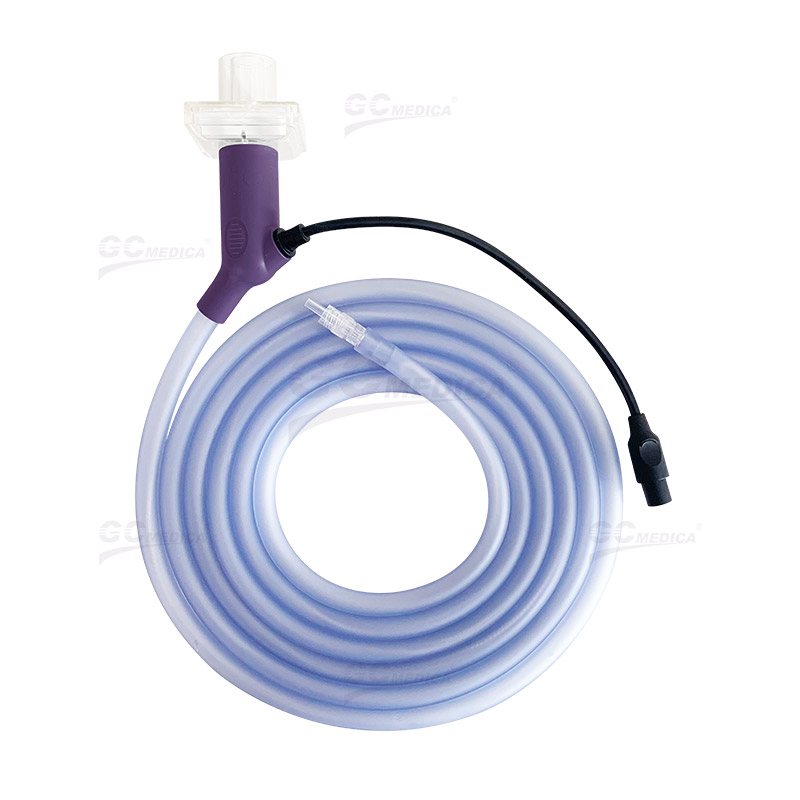
| Heated Insufflation Tubing | |
| Heated Insufflation Tubing | |
| Heated Insufflation Tubing |
Selecting Insufflator Tubing
When choosing insufflator tubing, consider the following factors:
Compatibility: Ensure the tubing is compatible with your surgical equipment and insufflation system.
Material: Opt for tubing made from medical-grade materials that are durable and resistant to kinking.
Size and Length: Select tubing with appropriate diameter and length to suit your procedural needs and patient anatomy.
Sterility: Use single-use, sterile tubing to minimize infection risks.
Flow Rate: Choose tubing that can accommodate the required gas flow rates for your procedures.
Maintaining Insufflator Tubing
Proper maintenance extends the life of insufflator tubing and ensures reliable performance:
Inspection: Regularly check tubing for signs of wear, such as cracks or leaks.
Cleaning: Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning, if applicable. Some tubing may be single-use only.
Storage: Store tubing in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and chemicals.
Disposal: Dispose of single-use tubing properly after each use to prevent cross-contamination.
Safety Considerations
Patient Monitoring: Continuously monitor patients for signs of insufflation-related complications, such as subcutaneous emphysema or gas embolism.
Training: Ensure all surgical staff are trained in the proper use and maintenance of insufflator tubing.
Adherence to Protocols: Follow institutional and manufacturer guidelines for tubing selection, usage, and maintenance.
By carefully selecting and maintaining insufflator tubing, healthcare providers can enhance surgical safety and effectiveness in minimally invasive procedures.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us