In critical care settings, providing timely and effective nutritional support is essential for patient recovery. Feeding tubes are a vital tool used in intensive care units (ICUs) to ensure that patients receive the necessary calories, vitamins, and minerals when they cannot eat by mouth. This article explains the role of feeding tubes in critical care, their types, best practices, and potential complications.
| ENFit Polyurethane Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
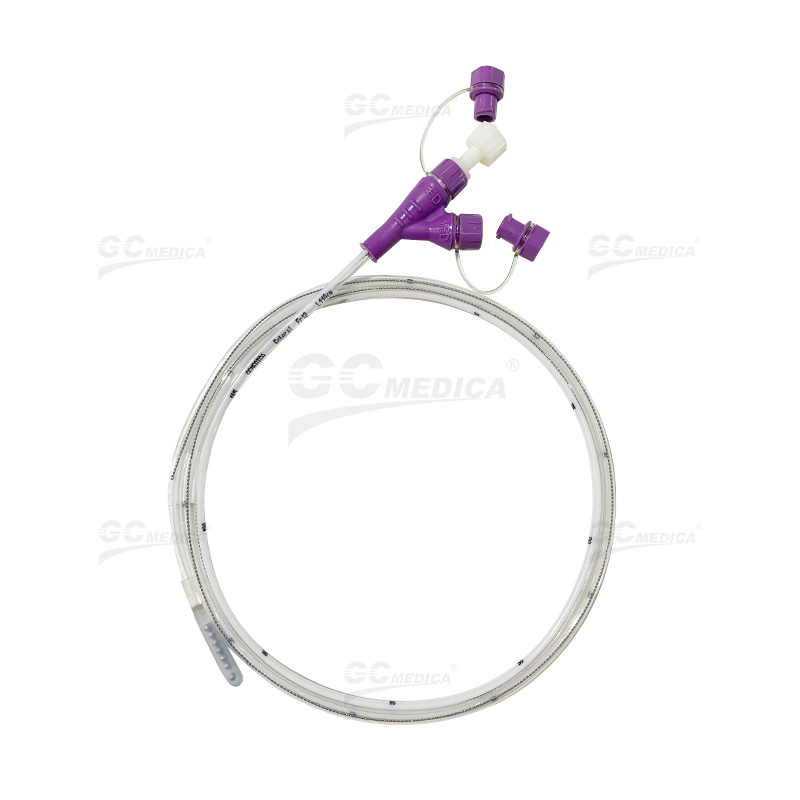
| ENFit Y-Port Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
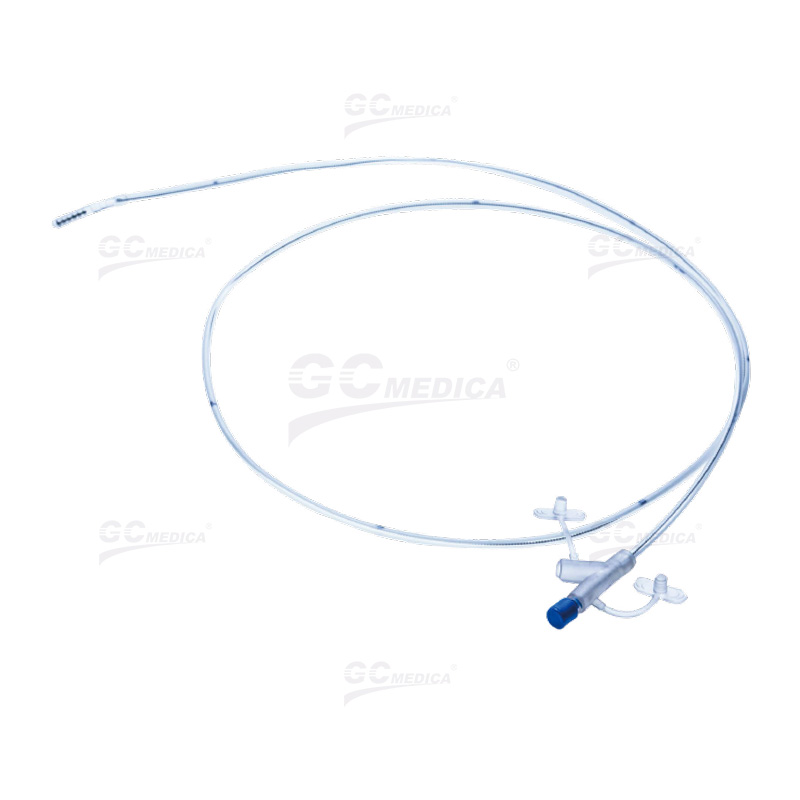
| Nasointestinal Feeding Tube | |
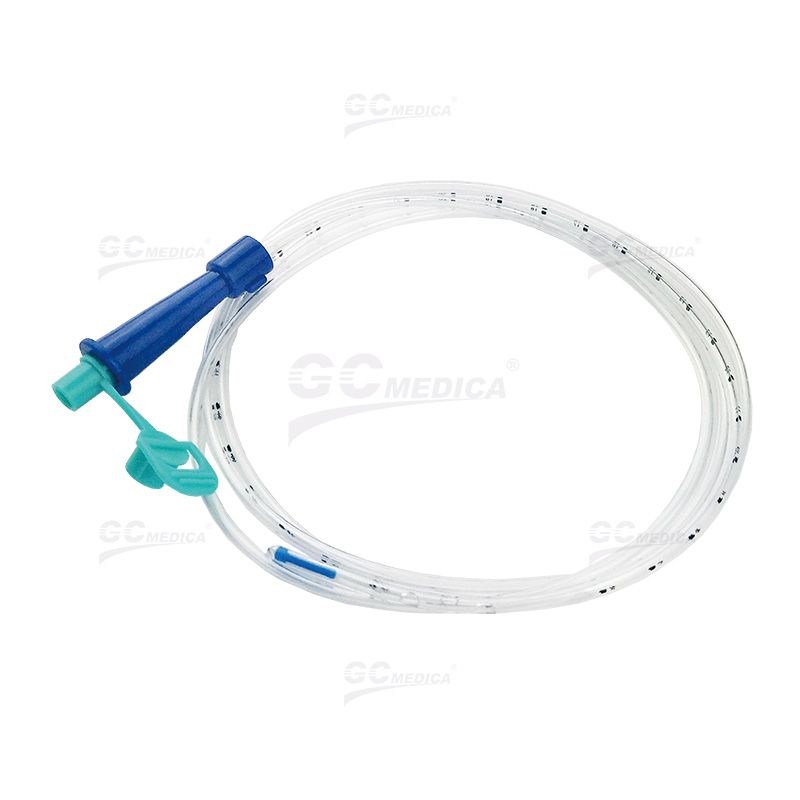
| Nasogastric (Ryles) Tubes |
The Importance of Nutrition in Critical Care
Patients in critical care often face severe illnesses, surgeries, or injuries that affect their ability to consume food normally. Proper nutrition supports immune function, wound healing, and overall recovery. Feeding tubes help maintain nutritional balance by delivering controlled amounts of liquid nutrition directly into the digestive system, ensuring that the body receives the essential nutrients it needs during a vulnerable time.
Types of Feeding Tubes Used in Critical Care
Different types of feeding tubes are chosen based on the patient’s condition and duration of nutritional support:
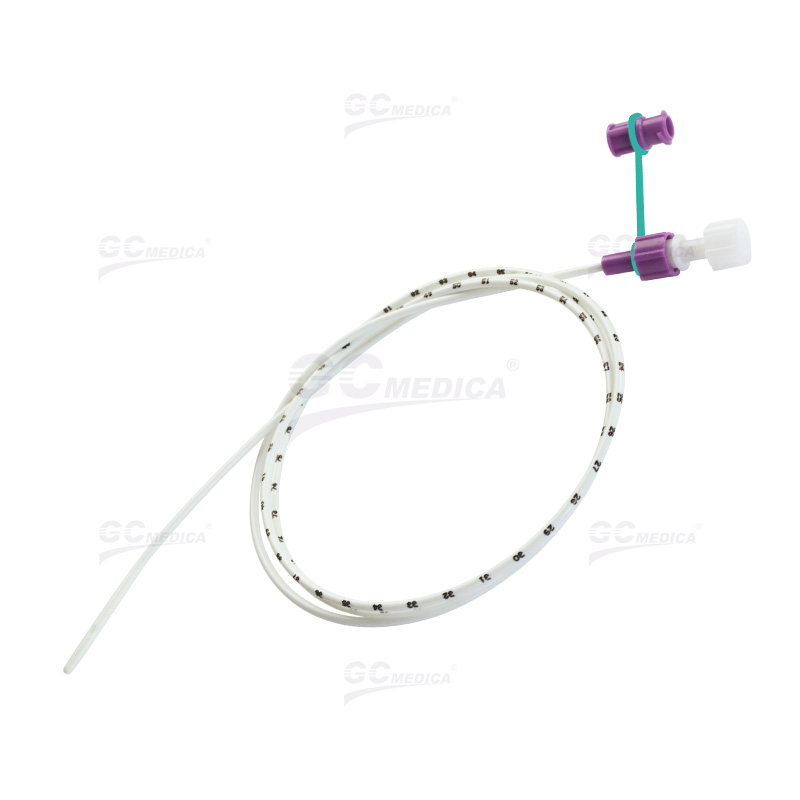
Nasogastric (NG) Tubes: Inserted through the nose and positioned in the stomach, NG tubes are commonly used for short-term feeding. Their ease of placement makes them ideal for patients expected to regain the ability to eat.
Gastrostomy Tubes (G-tubes): These are placed directly into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen. G-tubes are suited for patients requiring long-term nutritional support.
Jejunostomy Tubes (J-tubes): For patients with severe stomach dysfunction or those at risk of aspiration, J-tubes deliver nutrients directly into the small intestine.
Choosing the right type of feeding tube is a decision made by the healthcare team based on the patient’s overall condition and nutritional needs.
Best Practices for Managing Feeding Tubes in Critical Care
Effective management of feeding tubes in the ICU is critical for minimizing complications and promoting recovery. Key practices include:
Accurate Tube Placement: Verification using imaging or pH testing is essential to ensure the tube is correctly positioned. Misplacement can lead to severe complications.
Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers should continuously monitor the feeding tube site for signs of infection, leakage, or dislodgment. Early detection of issues allows for prompt intervention.
Scheduled Feeding Protocols: Depending on the patient’s tolerance, feeding can be administered as continuous slow infusions or in scheduled boluses. Tailoring the feeding schedule helps avoid gastrointestinal discomfort.
Proper Tube Maintenance: Routine flushing of the tube with water prevents blockages and ensures the tube remains clear. Meticulous cleaning of the insertion site is also crucial to reduce infection risks.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Nutritionists, nurses, and physicians should collaborate to review the patient’s nutritional plan regularly, adjusting caloric and fluid requirements based on ongoing assessments.
Potential Complications and Their Management
While feeding tubes are generally safe, they can sometimes lead to complications:
Infection: Local infections at the tube site can be minimized by adhering to strict hygiene and care protocols. Any signs of redness or discharge should be promptly evaluated.
Aspiration: There is a risk of nutritional contents entering the lungs if the tube is not correctly placed or if the patient experiences reflux. Careful monitoring and proper tube positioning help prevent this serious complication.
Blockage or Dislodgment: Regular flushing and secure fixation of the tube are necessary to prevent blockages or accidental removal.
Understanding these potential issues allows caregivers and healthcare professionals to act swiftly and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
Feeding tubes are an indispensable component of critical care, providing vital nutritional support when patients cannot eat on their own. By understanding the various types of feeding tubes, following best practices for their management, and being aware of potential complications, healthcare teams can significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Staying informed and vigilant is key in a critical care environment. Patients and caregivers benefit from clear communication with healthcare providers, ensuring that the nutritional needs of critically ill patients are met safely and effectively. With proper care and a well-coordinated approach, feeding tubes can play a pivotal role in the journey toward recovery.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us