Feeding tubes have become a critical medical tool, providing essential nutritional support to patients who are unable to meet their dietary needs through traditional eating. This article examines both the advantages and disadvantages of feeding tubes, offering an in-depth analysis to help patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals make informed decisions.
Understanding Feeding Tubes
Feeding tubes are medical devices that deliver nutrients directly to the stomach or small intestine. They are typically used when patients experience difficulties with swallowing, have impaired digestive systems, or are recovering from major surgeries. By bypassing the normal route of ingestion, these tubes ensure that patients receive the necessary calories, vitamins, and minerals to support healing and maintain overall health.
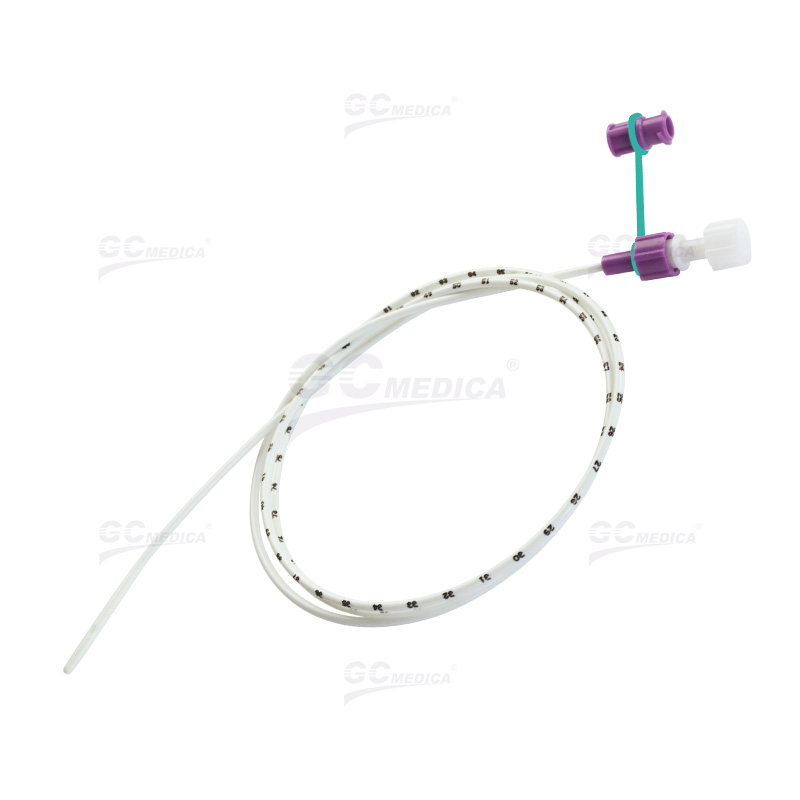
| ENFit Polyurethane Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
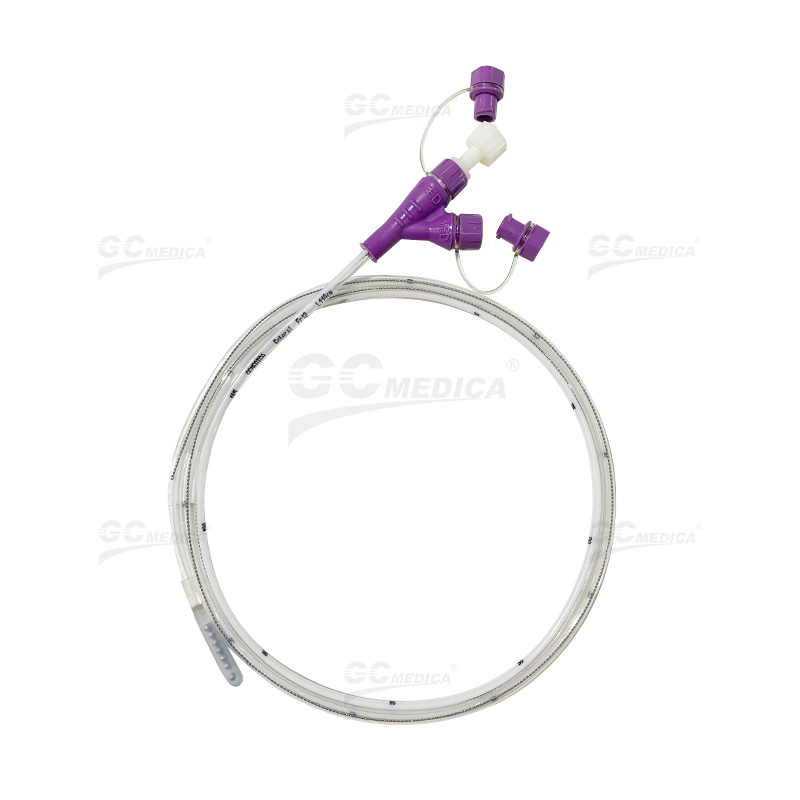
| ENFit Y-Port Nasogastric Feeding Tubes | |
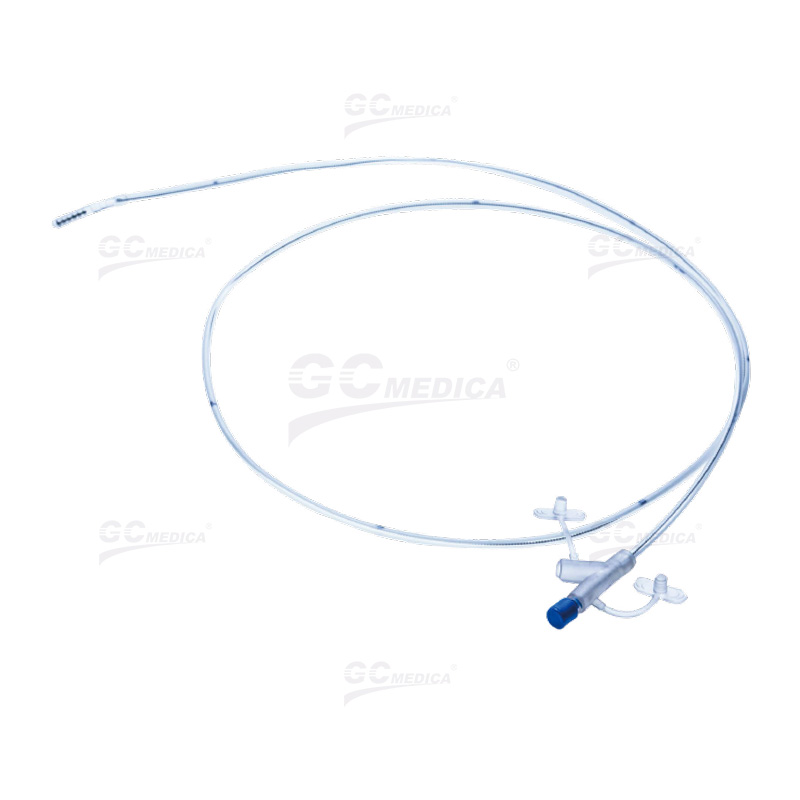
| Nasointestinal Feeding Tube | |
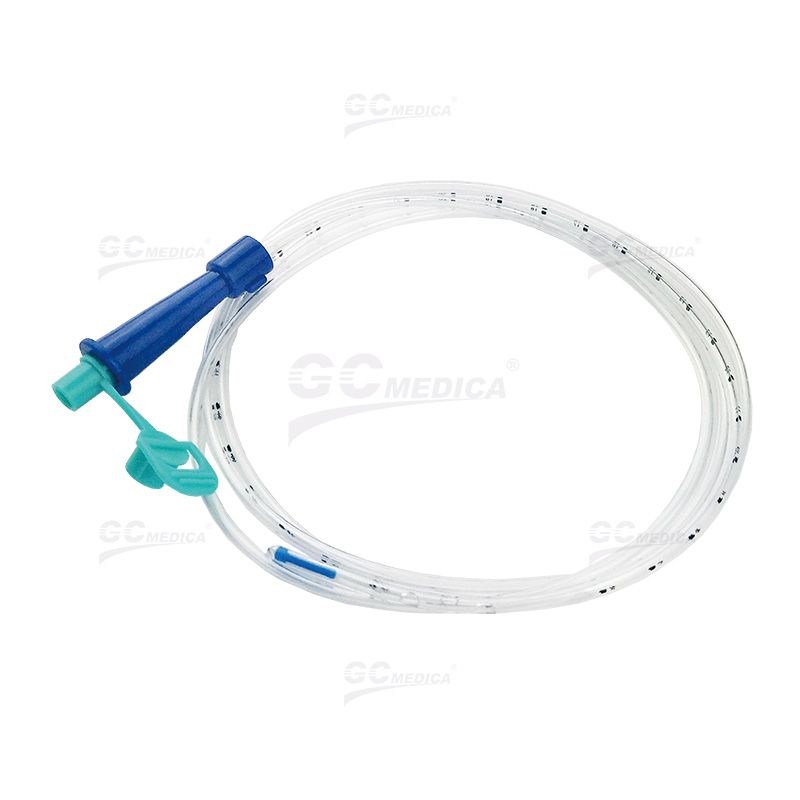
| Nasogastric (Ryles) Tubes |
The Pros of Feeding Tubes
1. Reliable Nutritional Support
One of the primary advantages of feeding tubes is their ability to provide consistent and controlled nutrition. This is particularly vital for patients who cannot consume food orally due to conditions like stroke, cancer, or neurological disorders. With precise nutrient formulations, feeding tubes help stabilize patients’ metabolic needs and prevent malnutrition.
2. Improved Recovery Rates
For patients recovering from surgery or critical illnesses, feeding tubes offer a dependable method of delivering nutrition that supports the healing process. Adequate nutrition is essential for wound healing, immune system function, and maintaining muscle mass, all of which contribute to faster recovery times.
3. Customizable Feeding Plans
Feeding tube regimens are highly customizable. Healthcare providers can tailor feeding schedules, formulas, and rates to meet each patient’s specific needs. This individualized approach ensures that the nutritional support is optimal for patients with varying metabolic rates and health conditions.
4. Enhanced Quality of Life
In many cases, feeding tubes enable patients to regain strength and improve their overall quality of life. By addressing nutritional deficiencies early, patients often experience better energy levels and improved outcomes, allowing them to participate more actively in their recovery process.
The Cons of Feeding Tubes
1. Risk of Infection
One of the significant drawbacks of feeding tubes is the potential for infections at the insertion site. Maintaining a sterile environment is crucial, and even with proper care, infections can occur, sometimes requiring additional medical intervention.
2. Discomfort and Lifestyle Limitations
Feeding tubes can cause physical discomfort or irritation, particularly around the insertion site. Patients may also experience a degree of lifestyle limitation, as the tube can interfere with daily activities or sleep. Psychological impacts, such as anxiety or self-consciousness about tube dependency, can also arise.
3. Potential for Blockages or Dislodgment
Feeding tubes require regular maintenance, including flushing to prevent blockages. Despite these efforts, blockages or accidental dislodgment can occur, leading to interruptions in feeding and potential health complications. This necessitates careful monitoring and frequent healthcare visits.
4. Cost and Resource Requirements
Long-term tube feeding can be expensive, involving costs for supplies, nutritional formulas, and regular professional care. For some patients, these financial considerations can be a burden, making it essential to weigh the benefits against the economic impact.
Balancing Benefits and Risks
Deciding whether a feeding tube is the right option involves a careful balance of benefits and risks. Patients and caregivers must consider:
Medical Necessity: Evaluating if the patient’s condition warrants tube feeding over other nutritional methods.
Risk Management: Implementing strict hygiene protocols and regular monitoring to minimize complications.
Lifestyle Considerations: Understanding how tube feeding may impact daily routines and seeking support to manage any associated stress.
Financial Implications: Assessing the long-term cost and exploring insurance or support programs that may help alleviate financial burdens.
Conclusion
Feeding tubes offer a lifesaving solution for patients who cannot obtain sufficient nutrition through traditional means. They provide reliable, customizable, and effective nutritional support that can significantly enhance recovery and quality of life. However, they also come with potential risks such as infections, discomfort, and additional costs.
An informed decision about tube feeding should involve detailed discussions with healthcare professionals, a thorough evaluation of the patient’s unique needs, and a careful weighing of the pros and cons. By staying educated and proactive, patients and caregivers can navigate the complexities of feeding tube therapy and work towards achieving the best possible health outcomes.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us