In critical care settings, maintaining airway patency in mechanically ventilated patients is paramount. Two primary methods are employed for endotracheal suctioning: the Open Suction System (OSS) and the Closed Suction System (CSS). Understanding the differences between these techniques is essential for optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring safety.
| |
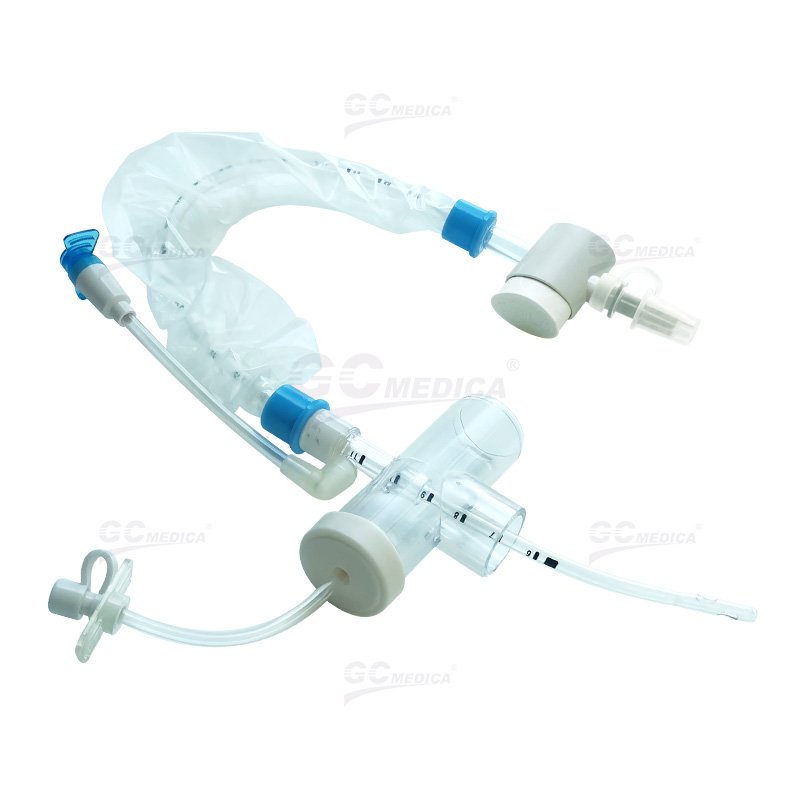
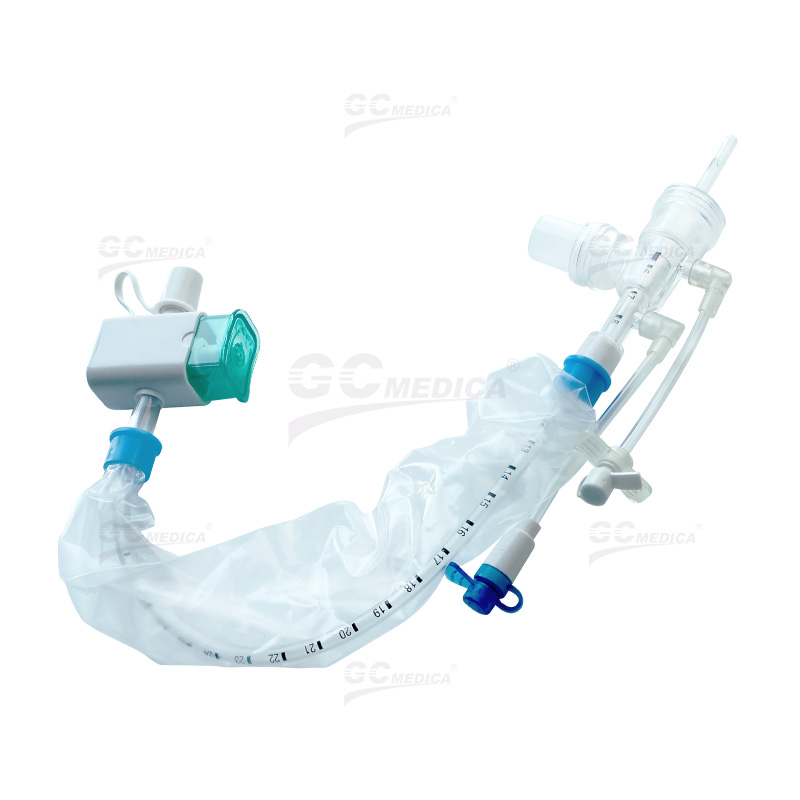
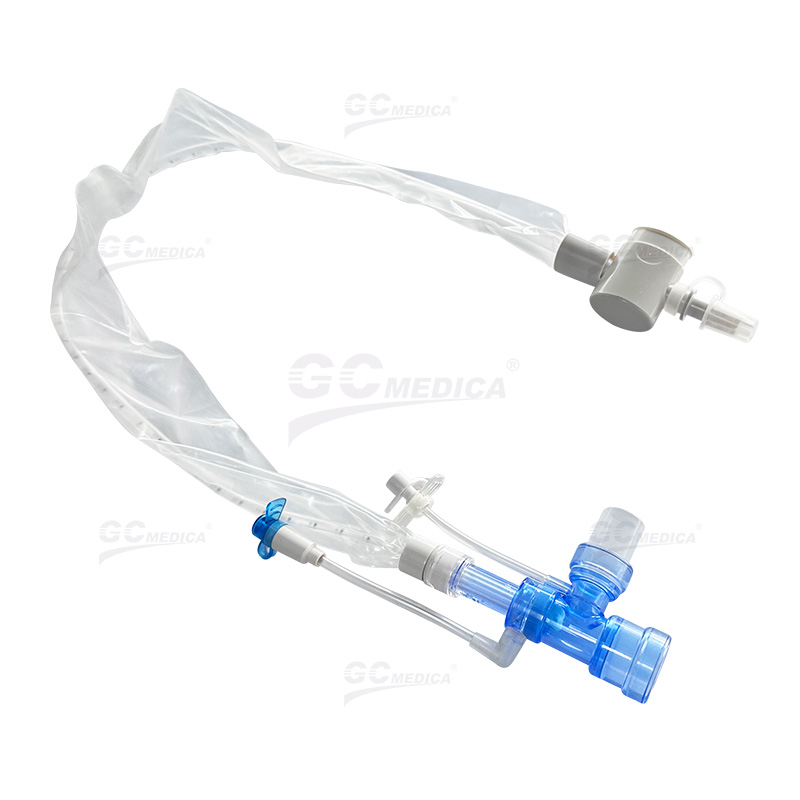
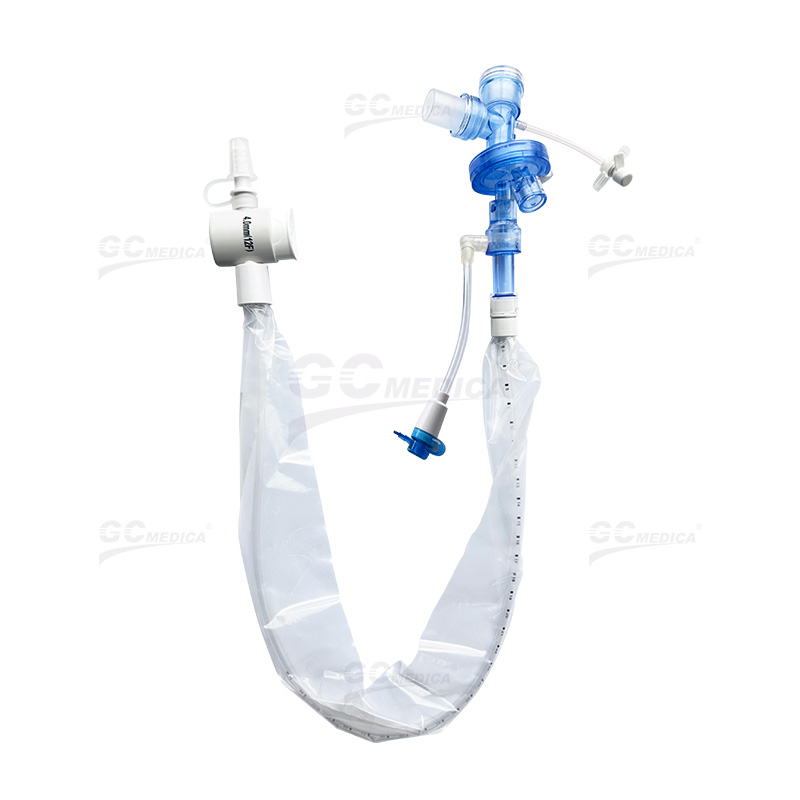
| Pedi Y Connector Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Trach T-piece Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Double Swivel Closed Suction Catheter | |
| 72H Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Multi-Port Closed Suction Catheter | |
Open Suction System (OSS)
The OSS involves disconnecting the patient from the ventilator to insert a sterile catheter into the endotracheal tube for secretion removal. While effective, this method has notable drawbacks:
Interruption of Ventilation: Disconnecting the ventilator can lead to alveolar collapse and hypoxemia.
Infection Risk: Exposure of the airway increases the potential for contamination and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
Hemodynamic Instability: The procedure can cause fluctuations in heart rate and blood pressure.
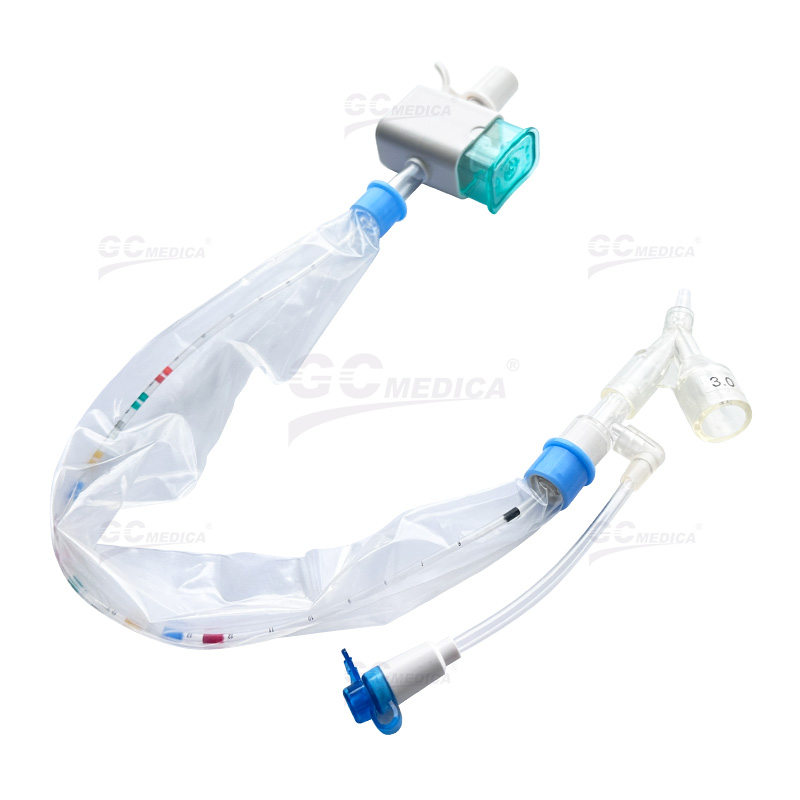
Closed Suction System (CSS)
The CSS allows for suctioning without disconnecting the ventilator, using a catheter enclosed within a sterile sheath. Advantages of this system include:
Continuous Ventilation: Maintains positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and oxygenation during the procedure.
Reduced Infection Risk: Minimizes exposure to pathogens, lowering the incidence of VAP.
Enhanced Safety: Decreases hemodynamic disturbances and cross-contamination risks.
Clinical Evidence
A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing OSS and CSS found no significant difference in VAP rates between the two methods. However, CSS demonstrated benefits in maintaining oxygenation and reducing hemodynamic alterations during suctioning.
Practical Considerations
When choosing between OSS and CSS, healthcare providers should consider:
Patient Stability: CSS is preferable for patients with high oxygen requirements or hemodynamic instability.
Infection Control Policies: Facilities aiming to reduce VAP rates may favor CSS due to its enclosed design.
Resource Availability: OSS may be more cost-effective but requires strict adherence to sterile techniques to mitigate infection risks.
Conclusion
Both OSS and CSS have roles in critical care, with CSS offering advantages in maintaining ventilation and reducing certain risks. Clinical judgment, patient condition, and institutional protocols should guide the selection of the appropriate suctioning technique.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us