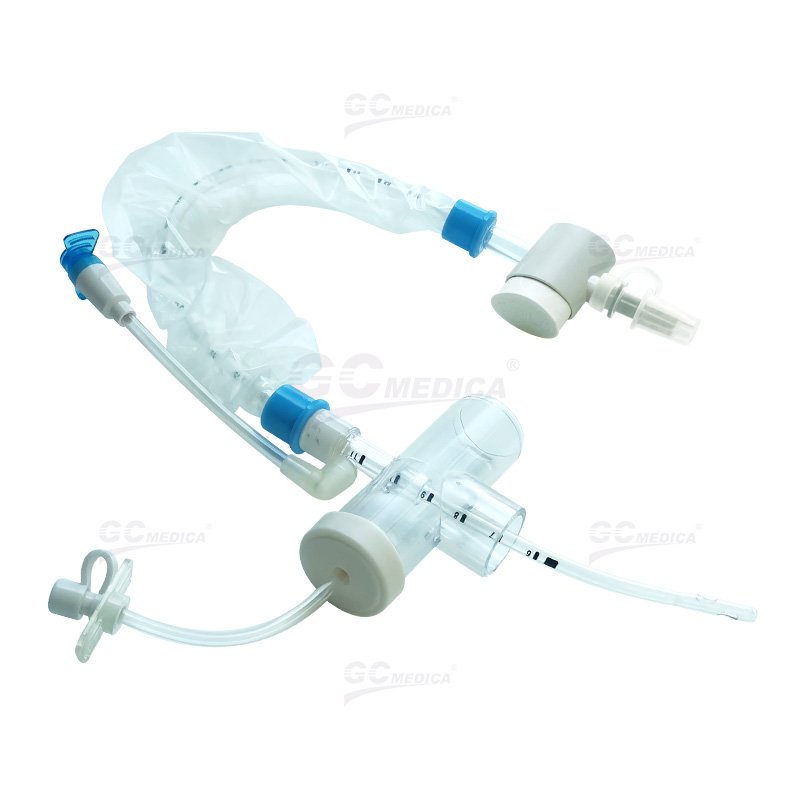
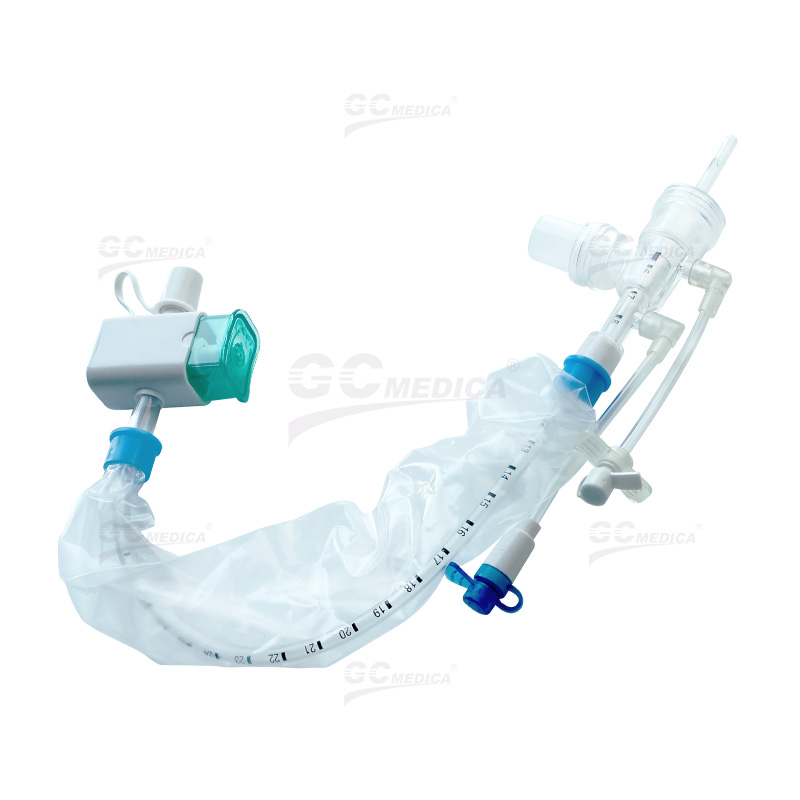
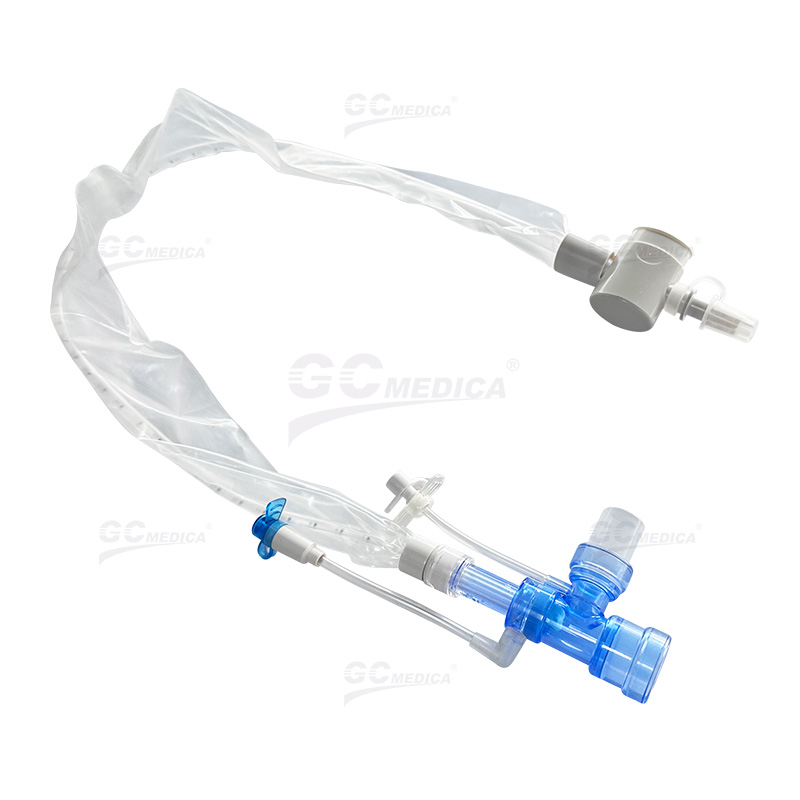
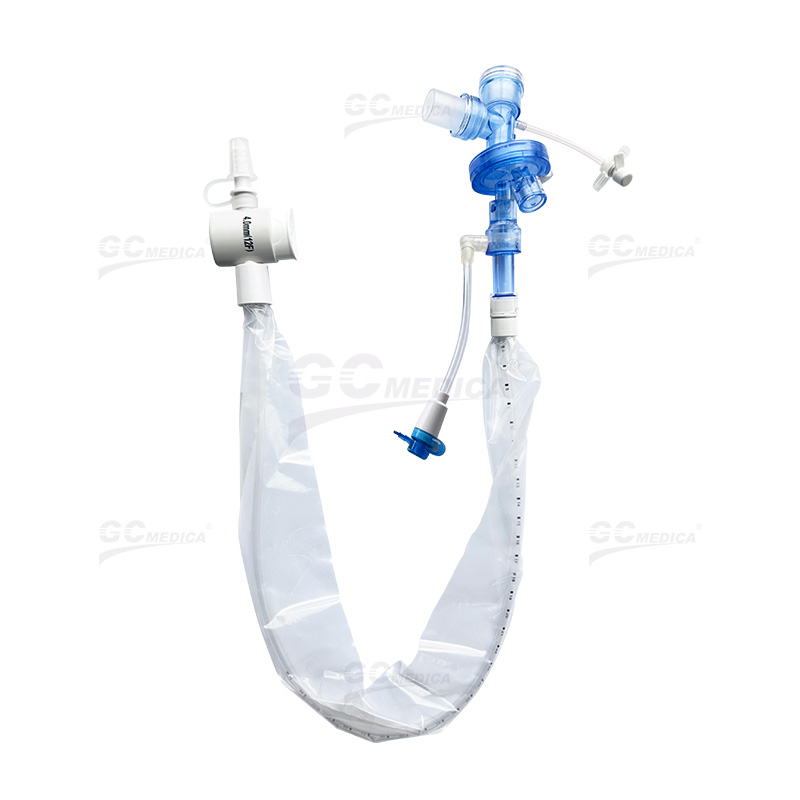
Efficient airway management is critical for patients receiving mechanical ventilation, and a closed suction catheter system plays an essential role in maintaining respiratory stability while minimizing complications. This system enables clinicians to suction secretions without disconnecting the ventilator circuit, ensuring continuous oxygenation and reducing infection risks. Below are best practices for optimizing the use of a closed suction catheter system in airway management.
Understanding the Closed Suction Catheter System
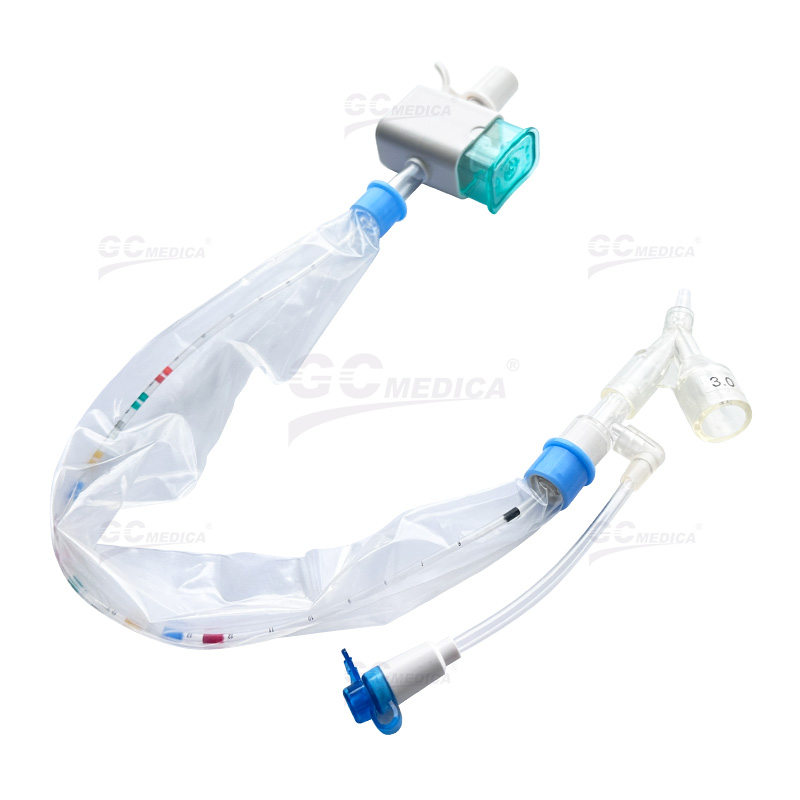
A closed suction catheter system is designed to allow suctioning of airway secretions while the patient remains connected to the ventilator. This method preserves positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and minimizes fluctuations in oxygen levels. Its enclosed design reduces the exposure of both the patient and healthcare providers to potential pathogens, thereby enhancing infection control within intensive care settings.
| Pedi Y Connector Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Trach T-piece Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Double Swivel Closed Suction Catheter | |
| 72H Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Multi-Port Closed Suction Catheter |
Best Practices for Use
1. Staff Training and Competency
Thorough training is crucial for all healthcare personnel involved in airway management. Regular educational sessions should be conducted to ensure that clinicians are proficient in operating the closed suction system. Training should emphasize:
Correct handling and insertion techniques.
Recognizing indications for suctioning.
Understanding the system’s safety features to avoid accidental disconnections.
Responding promptly to any complications during the procedure.
2. Adherence to Protocols
Standardized protocols help ensure consistency and safety in airway management. Institutions should develop and implement guidelines that outline:
The appropriate frequency and duration of suctioning based on patient condition.
Steps for maintaining system integrity during suctioning procedures.
Criteria for when to perform suctioning to optimize patient comfort and prevent secretion build-up.
Protocols for documenting each suction event to monitor patient progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
3. Regular Equipment Maintenance
To guarantee optimal performance, it is essential to inspect and maintain the closed suction catheter system regularly. Daily checks should include:
Verifying the integrity of the suction catheter and tubing.
Ensuring that all components are free from blockages or damage.
Replacing single-use components as recommended by clinical guidelines.
Implementing routine maintenance schedules to prevent malfunctions and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
4. Infection Control Measures
Maintaining strict infection control is paramount in critical care environments. The closed suction system inherently reduces the risk of cross-contamination; however, additional measures should be enforced:
Utilize appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during procedures.
Follow aseptic techniques during insertion and removal of the catheter.
Discard or sterilize components according to established protocols to minimize the risk of ventilator-associated infections.
Monitor patient outcomes to promptly identify and address any signs of infection.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Real-time monitoring of patient oxygenation and ventilation parameters during suctioning is essential. Healthcare providers should:
Use continuous pulse oximetry and capnography to detect any changes in patient status.
Adjust ventilator settings as needed to compensate for any temporary fluctuations during suctioning.
Document any adverse events and review them regularly to improve future practices.
Engage in multidisciplinary discussions to update protocols based on emerging evidence and clinical experience.
Conclusion
Implementing best practices for the closed suction catheter system is vital for enhancing airway management in mechanically ventilated patients. Through comprehensive staff training, adherence to standardized protocols, regular equipment maintenance, stringent infection control measures, and continuous monitoring, healthcare facilities can significantly improve patient outcomes. By prioritizing these strategies, clinicians can ensure efficient and safe respiratory care while minimizing the risks associated with mechanical ventilation.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us