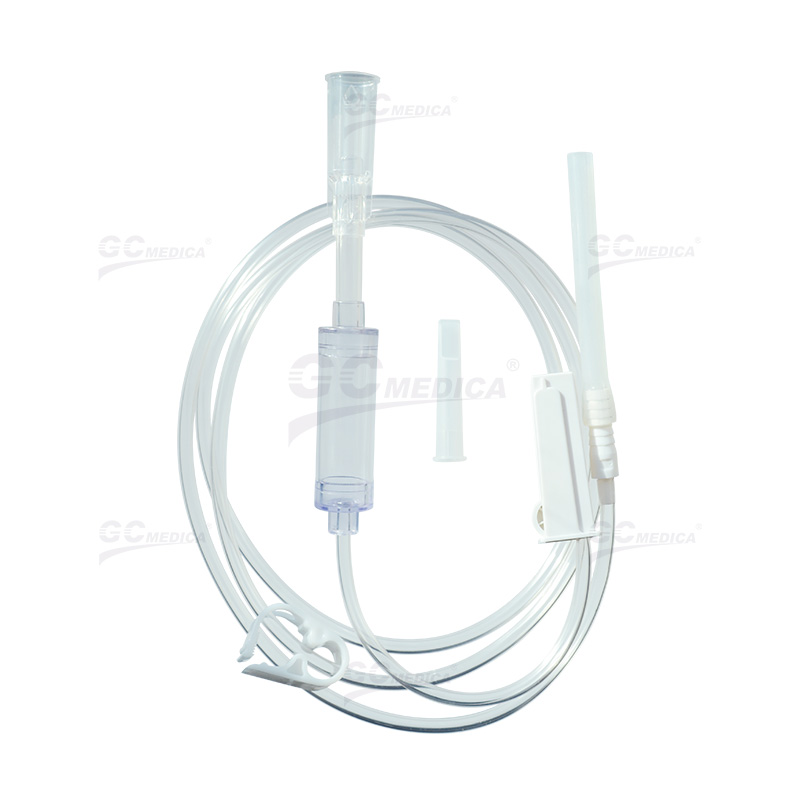
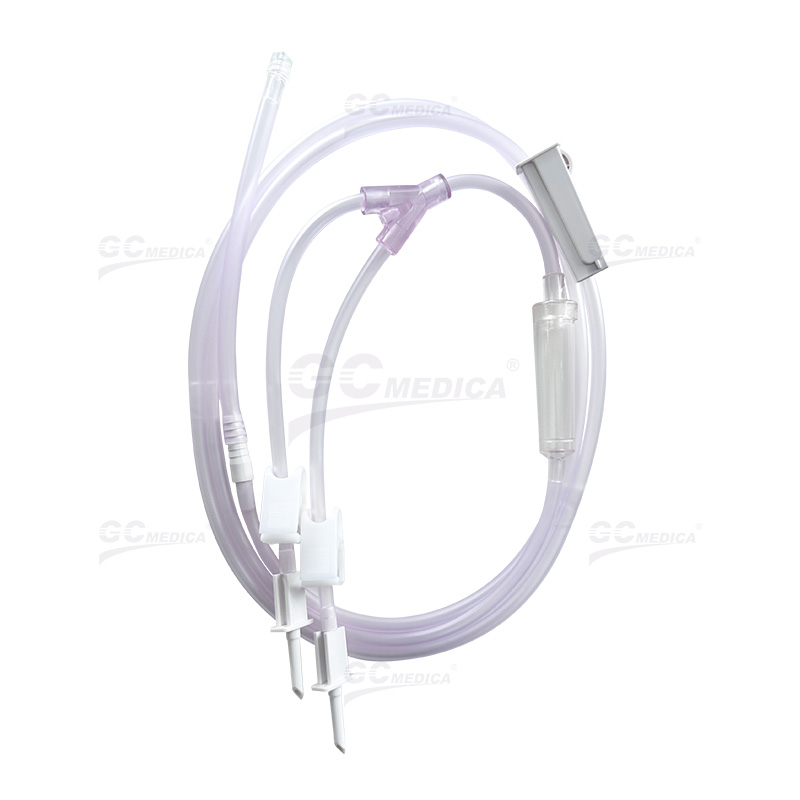
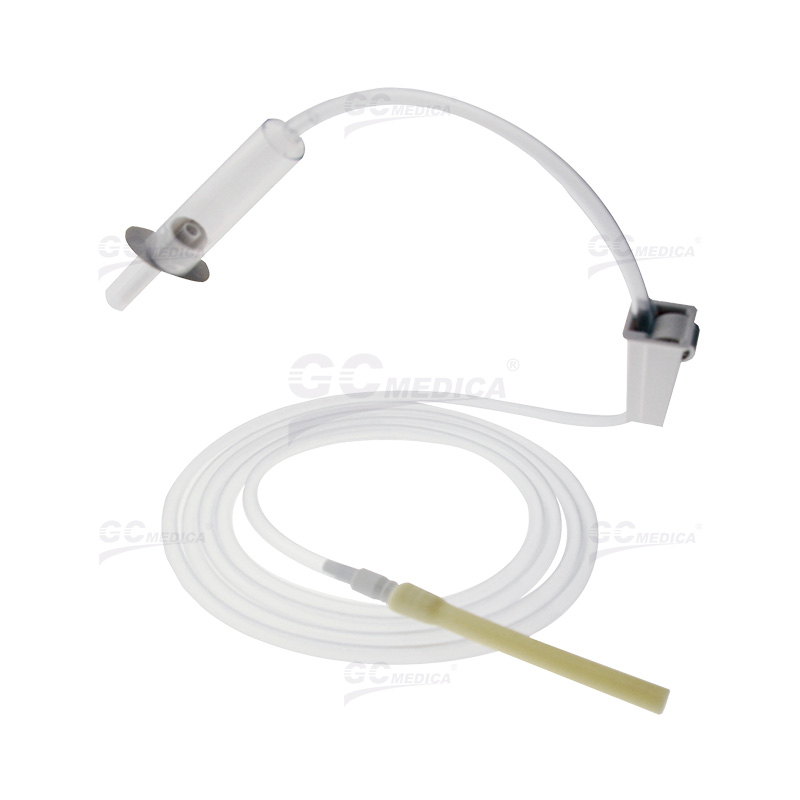
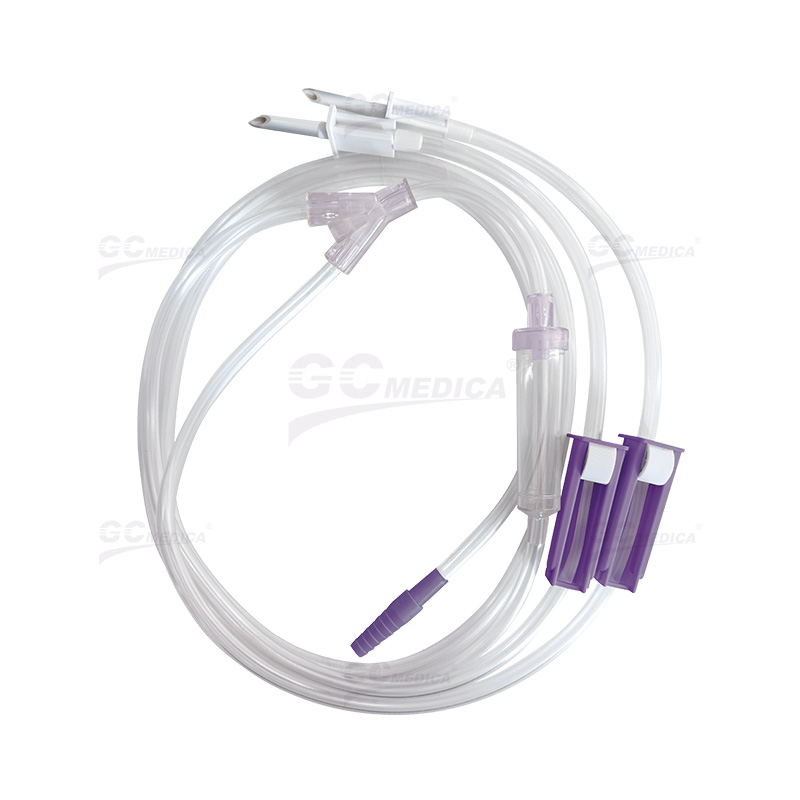
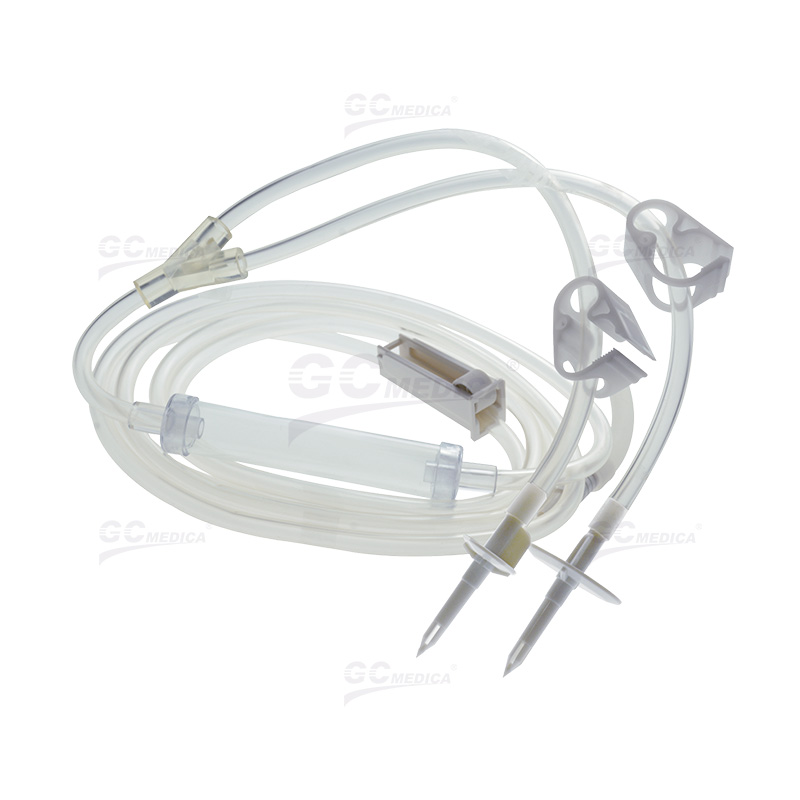
Bladder irrigation is a pivotal procedure in urological care, employed to prevent or manage complications such as blood clot formation following surgeries like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Central to this procedure is the bladder irrigation tubing, which facilitates the continuous or intermittent flushing of the bladder with sterile solutions. Proper selection and usage of this tubing are essential for patient safety and the efficacy of the irrigation process.
Understanding Bladder Irrigation Tubing
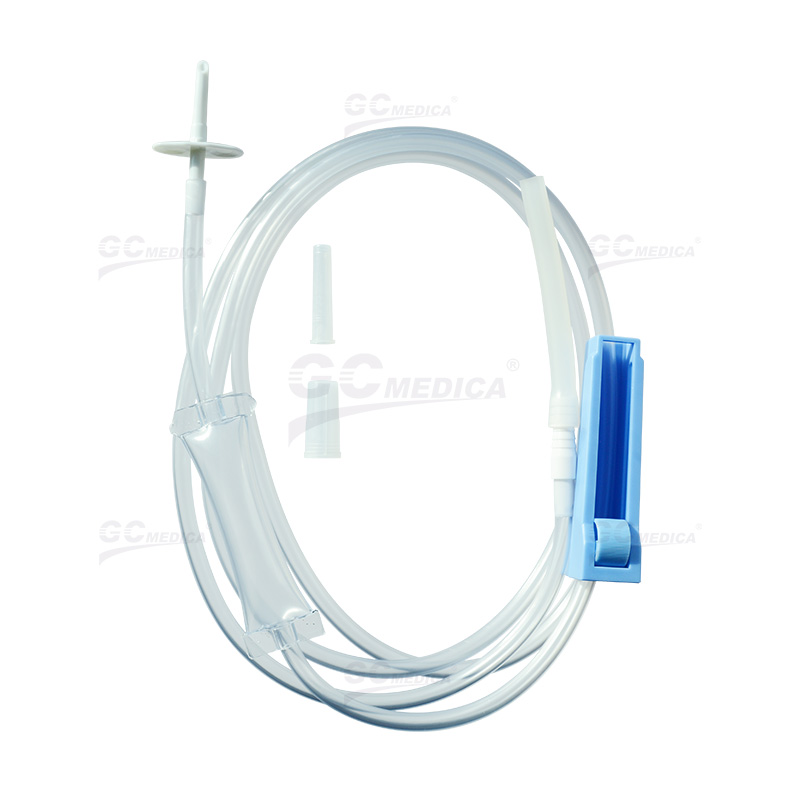
Bladder irrigation tubing serves as the conduit for sterile irrigation solutions introduced into the bladder to prevent clot retention and ensure catheter patency. This process is crucial in maintaining urinary flow and reducing the risk of infection or other complications.
| MAPLE Bladder Irrigation Kit | |
| PEONY Bladder Irrigation Kit | |
| SANDALWOOD Bladder Irrigation Kit | |
| FREESIA Bladder Irrigation Kit | |
| JASMINE Bladder Irrigation Kit | |
| DAFFODIL Bladder Irrigation Kit |
Types of Bladder Irrigation
There are primarily three methods of bladder irrigation:
Continuous Bladder Irrigation (CBI): Involves the nonstop infusion of a sterile solution into the bladder, commonly used postoperatively to prevent blood clot formation.
Intermittent Bladder Irrigation: Performed at scheduled intervals to clear debris or clots from the bladder.
Manual Bladder Irrigation: Utilized on an as-needed basis, often when immediate intervention is required to clear obstructions.
Selecting the Appropriate Bladder Irrigation Tubing
When choosing bladder irrigation tubing, consider the following factors:
Compatibility: Ensure the tubing is compatible with the existing catheter system to prevent leaks or disconnections.
Material Quality: Opt for tubing made from medical-grade, biocompatible materials to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Length and Diameter: Select tubing with appropriate length and internal diameter to facilitate adequate flow rates without causing patient discomfort.
Sterility: Use pre-sterilized tubing to reduce the risk of introducing infections during the irrigation process.
Proper Usage of Bladder Irrigation Tubing
Adhering to best practices in the usage of bladder irrigation tubing is vital for patient safety and the effectiveness of the procedure:
Aseptic Technique: Always employ aseptic techniques when handling irrigation equipment to prevent infections.
System Setup:
Close all clamps on the irrigation tubing before connecting.
Hang the irrigation solution bag on an intravenous pole, ensuring it is positioned above the bladder level to facilitate gravity-assisted flow.
Prime the tubing by allowing the solution to fill it completely, eliminating any air pockets.
Connect the tubing securely to the catheter's irrigation port.
Initiating Irrigation:
Open the clamp to begin the flow of the irrigation solution.
Adjust the flow rate according to medical orders, ensuring it is sufficient to prevent clot formation without causing bladder overdistension.
Monitoring:
Regularly observe the color and consistency of the outflow to assess the effectiveness of the irrigation.
Ensure that the volume of the irrigant infused matches the volume recovered to detect any discrepancies promptly.
Troubleshooting:
If the outflow is obstructed or the patient experiences discomfort, temporarily halt the irrigation and assess the system for kinks, clots, or other issues.
Manual irrigation may be necessary to clear any blockages before resuming continuous irrigation.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance of the irrigation system is essential:
Regular Assessment: Frequently check the irrigation setup for signs of leaks, disconnections, or contamination.
Solution Replacement: Replace irrigation solutions as per institutional protocols to prevent microbial growth.
Documentation: Accurately document the volume of irrigation solution infused and recovered, as well as any observations related to the procedure.
Conclusion
Bladder irrigation tubing plays a critical role in urological care, particularly in preventing postoperative complications such as blood clot formation. Selecting appropriate tubing and adhering to proper usage protocols are paramount to ensuring patient safety and the success of the irrigation process. Healthcare professionals must be well-versed in the selection criteria, setup procedures, and maintenance practices associated with bladder irrigation systems to provide optimal care.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us