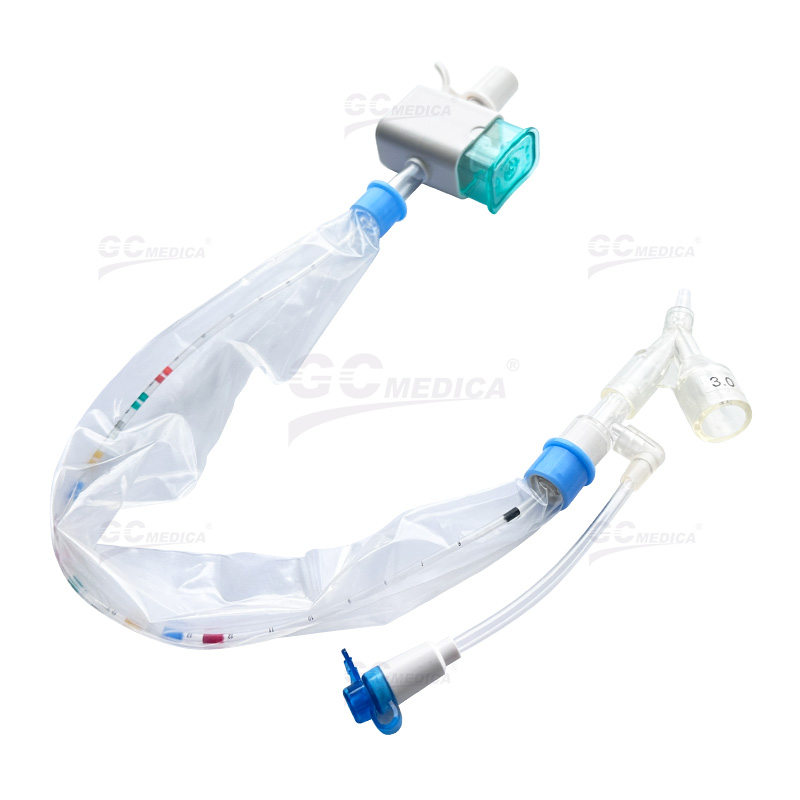
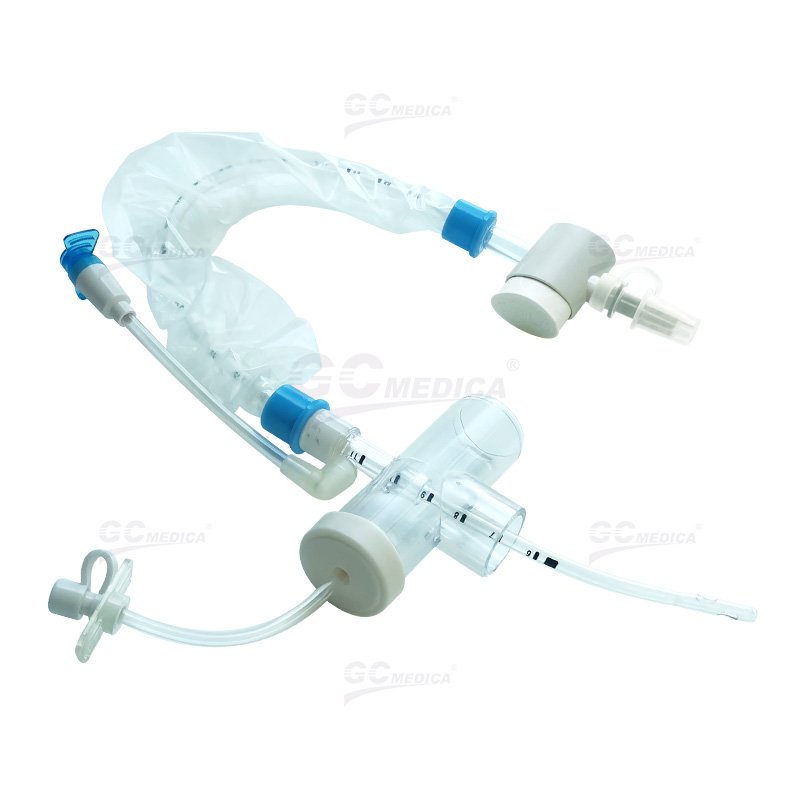
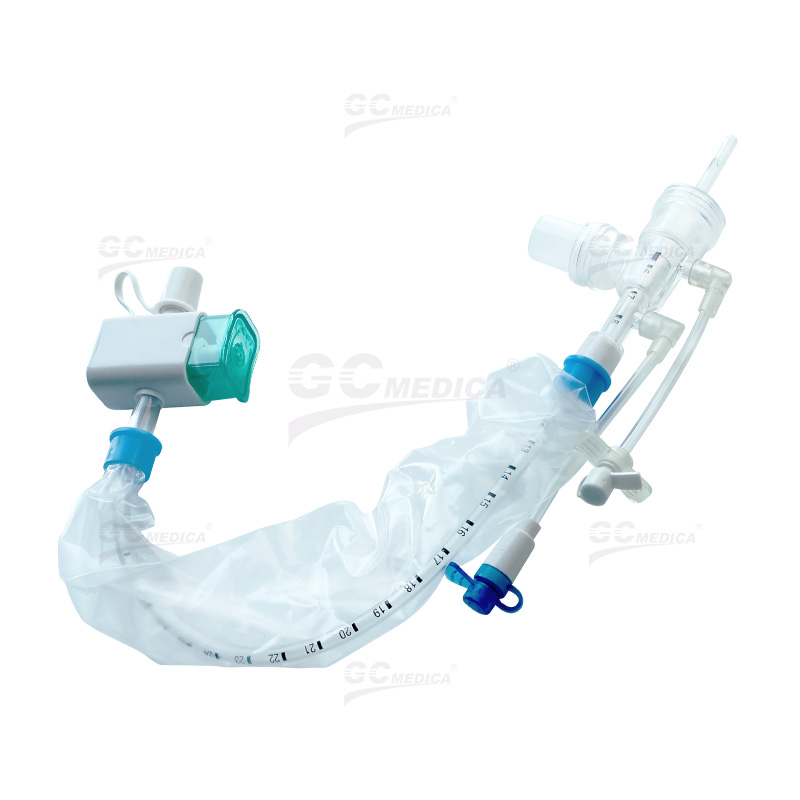
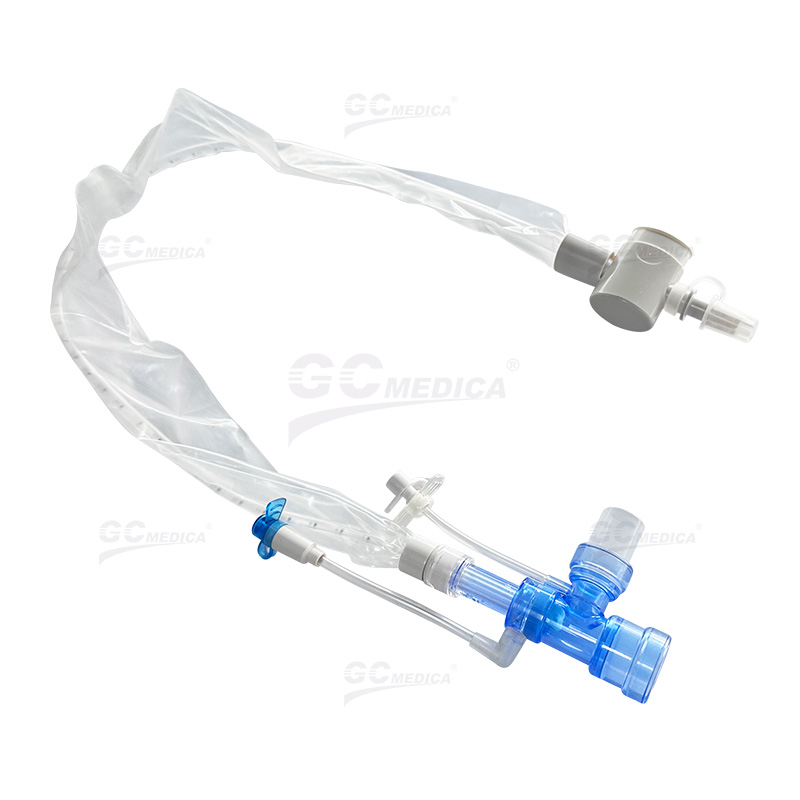
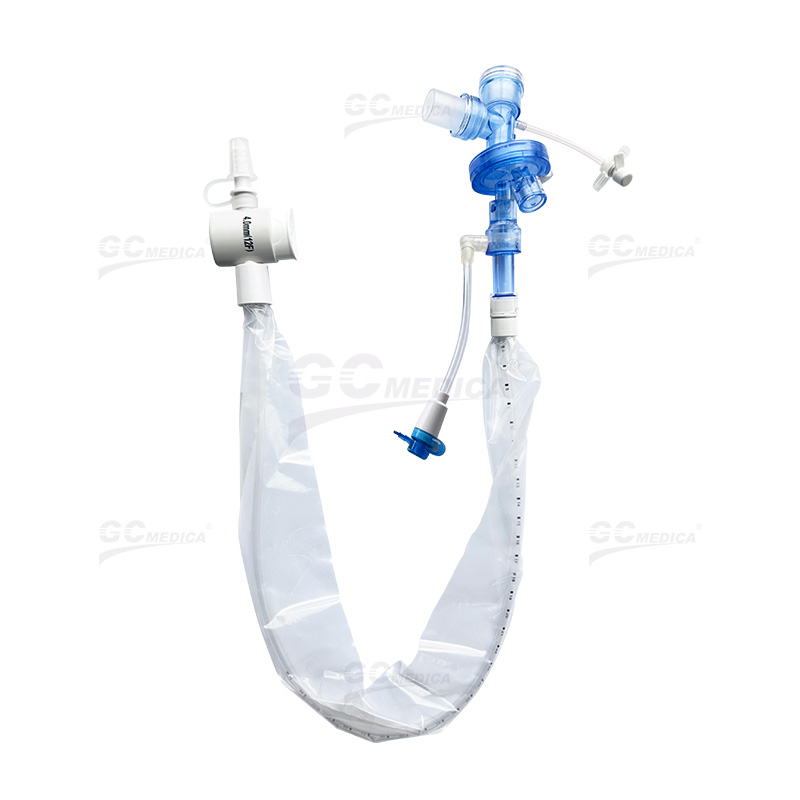
In critical care settings, maintaining airway hygiene for intubated patients is essential. Closed suction catheters allow clinicians to remove secretions safely without disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, thereby reducing the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia. One of the most important factors in choosing a closed suction catheter is its size.
Understanding Closed Suction Catheters
A closed suction catheter is a device integrated into the ventilator circuit, designed for continuous access to the airway while preserving a sterile, closed system. The catheter is housed within a sheath, allowing for periodic suctioning of secretions without compromising the ventilator's pressure and oxygenation settings.
| |
| Pedi Y Connector Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Trach T-piece Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Double Swivel Closed Suction Catheter | |
| 72H Closed Suction Catheter | |
| Multi-Port Closed Suction Catheter | |
The Role of Catheter Size
Catheter size, typically measured in French gauge (Fr), is critical to both suction efficiency and patient safety. Smaller catheters (e.g., 12–14 Fr) are often used for patients with smaller endotracheal tubes or for those who require less aggressive suctioning. Larger sizes (e.g., 16–18 Fr) offer a wider lumen for the removal of thicker secretions but may not be suitable for all patients, as an oversized catheter can impair ventilation or cause mucosal trauma.
Key Considerations for Selecting the Right Size
Several factors influence the optimal closed suction catheter size:
Patient Anatomy and Endotracheal Tube Diameter: The catheter’s outer diameter must be compatible with the patient’s endotracheal tube to avoid compromising the airway. A general rule is to use a catheter size that does not exceed 50% of the inner diameter of the tube.
Secretion Characteristics: Patients with copious or thick secretions may benefit from a larger catheter that offers increased suction flow. Conversely, for patients with minimal or thin secretions, a smaller catheter minimizes airway irritation.
Ventilator Settings and Lung Mechanics: The closed system’s integrity is paramount. A catheter that is too large might lead to loss of positive pressure, potentially affecting oxygenation and ventilation.
Clinical Protocols and Manufacturer Recommendations: Many healthcare facilities have standardized protocols for catheter sizes based on evidence and manufacturer guidelines. Following these protocols ensures consistency and safety in patient care.
Benefits of Correct Catheter Sizing
Using the right closed suction catheter size ensures efficient secretion removal while minimizing potential complications such as mucosal injury, hypoxia, or ventilator disconnections. Proper catheter sizing helps maintain effective ventilation and optimizes the overall respiratory care provided in intensive care units.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate closed suction catheter size is a critical decision that directly impacts patient safety and the efficiency of airway management in the ICU. By considering factors such as endotracheal tube size, secretion consistency, and ventilator parameters, healthcare professionals can ensure optimal outcomes. As respiratory care technology advances, the emphasis on precise catheter sizing remains central to reducing complications and enhancing patient care in critical settings.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us




 GCMEDICA Closed Suction Catheters Online Promotion
GCMEDICA Closed Suction Catheters Online Promotion